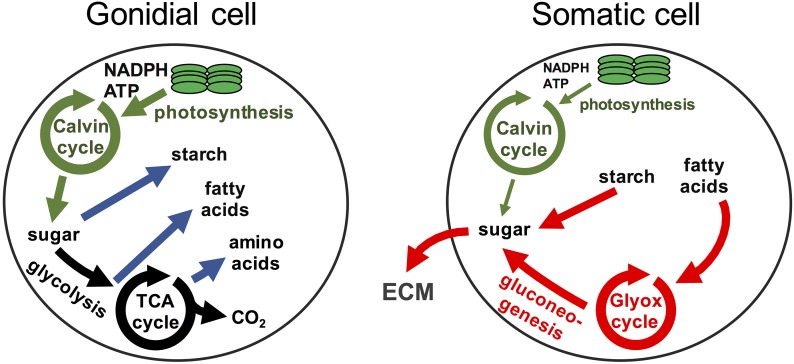
Figure 10.
Model for gonidial and somatic cell metabolic specialization. Gonidia (left) have active photosynthesis as well as production of new photosynthetic machinery to support growth metabolism with net production of starch, lipids, and amino acids. Glycolysis and the TCA cycle are the preferred route for carbon flow in gonidial cells. Somatic cells (right) maintain active photosynthesis at somewhat reduced levels compared to gonidia, and with reduced production of new photosynthetic machinery. Lipids are broken down and metabolized through the glyoxylate cycle and gluconeogenesis to make sugars. Starch is also catabolized into sugar monomers which are used as substrates to produce excreted ECM glycoproteins. ECM, extracellular matrix; TCA, tricarboxylic acid.