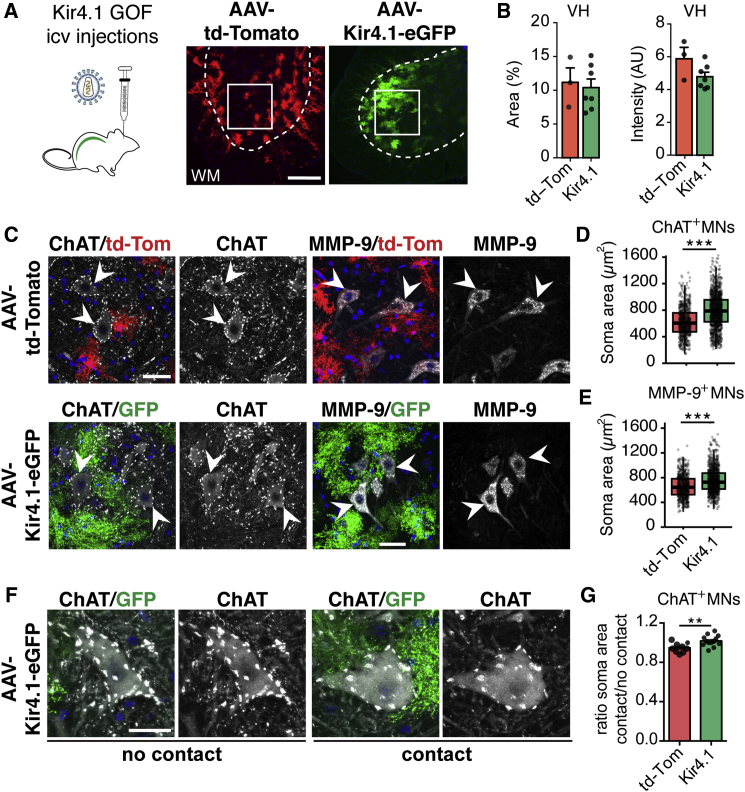
Figure 5.
Kir4.1 Viral-Mediated Overexpression Is Sufficient to Increase MN Size
(A and B) Left: schematic of intracerebroventricular injections in neonatal mice (P2–P3) of AAV-encoding Kir4.1-eGFP or control td-Tomato vectors for gain-of-function (GOF) experiments (A). Right: viral transduction of ventral spinal cord with AAV-td-Tomato or AAV-Kir4.1-eGFP quantified in (B) (n = 3–7 mice/group, mean ± SEM, Mann-Whitney test).
(C) ChAT (right) and MMP-9 (left) immunofluorescent staining in the ventral spinal cord of AAV-td-Tomato and AAV-Kir4.1-eGFP-injected mice.
(D and E) Quantifications of ChAT+ (D) and MMP-9+ (E) MN soma area in P60 mice (2 months post injection) (n = 9–13 mice/group, 70–100 MNs counts/animal, boxplot, Mann-Whitney test, scale bar, 40 μm).
(F) Example of MNs in contact (right) or not (left) with Kir4.1-overexpressing AS.
(G) Ratio of soma area of MN contacting/non-contacting transduced AS (n = 9–13 mice/group, mean ± SEM, Mann-Whitney test). ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001. Edges of boxplots denote interquartile range (25th –75th percentile) with whiskers denoting 1.5 times the interquartile range and black line denoting the median value.