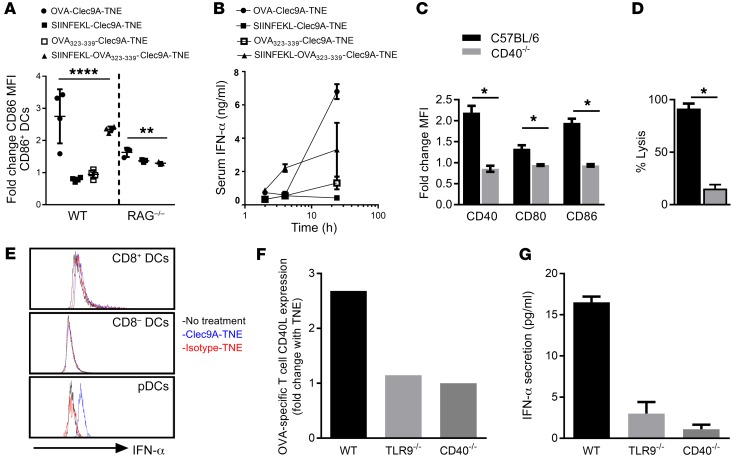
Figure 3. OVA-Clec9A-TNE–mediated DC activation and IFN-α production require CD4+ and CD8+ T cell epitope presentation and CD40L-CD40 crosstalk.
(A) C57BL/6 or RAG1–/– mice were injected i.v. with OVA-Clec9A-TNE, SIINFEKL-Clec9A-TNE, OVA323–339-Clec9A-TNE, or SIINFEKL-OVA323–339-Clec9A-TNE. Six hours later, surface expression of CD86 by CD8+ DCs was analyzed by flow cytometry (n = 3–8 from 2 separate experiments). (B) C57BL/6 mice were injected i.v. with OVA-Clec9A-TNE, SIINFEKL-Clec9A-TNE, OVA323–339-Clec9A-TNE, SIINFEKL-OVA323–339-Clec9A-TNE, or OVA-isotype-TNE. Serum was collected 2, 4, and 24 hours after injection, and IFN-α levels were quantified by ELISA (n = 4). (C) C57BL/6 or CD40–/– mice were injected i.v. with OVA-Clec9A-TNE. Six hours later, surface expression of CD40, CD80, and CD86 by CD8+ DCs was analyzed by flow cytometry (n = 4). (D) C57BL/6 or CD40–/– mice were adoptively transferred with equal numbers of unpulsed CFSElo and SIINFEKL-pulsed CFSEhi target cells 6 days after i.v. injection with OVA-Clec9A-TNE. The percentage of SIINFEKL peptide–specific lysis in spleen is depicted (n = 4). (E) Splenic CD11c+ DCs were purified from C57BL/6 mice, then cultured for 5 hours with OT-I OVA-specific CD8+ and OT-II OVA-specific CD4+ T cells, in the presence or absence of OVA-Clec9A-TNE or OVA-isotype-TNE. Histograms depict intracellular IFN-α levels in gated DC populations. Splenic CD11c+ DCs were purified from C57BL/6 (WT), CD40–/–, or TLR9–/– mice, then cultured for 24 hours with OT-I OVA-specific CD8+ and OT-II OVA-specific CD4+ T cells, in the presence or absence of OVA-Clec9A-TNE or OVA-isotype-TNE. (F) Increase in CD40L expression by OT-II cells in the presence of OVA-Clec9A-TNE relative to no TNE control. (G) Increase in IFN-α secretion into cell culture supernatant in the presence of OVA-Clec9A-TNE relative to no TNE control. Representative data from 6 mice are shown. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ****P < 0.0001 by Tukey’s multiple-comparisons test.