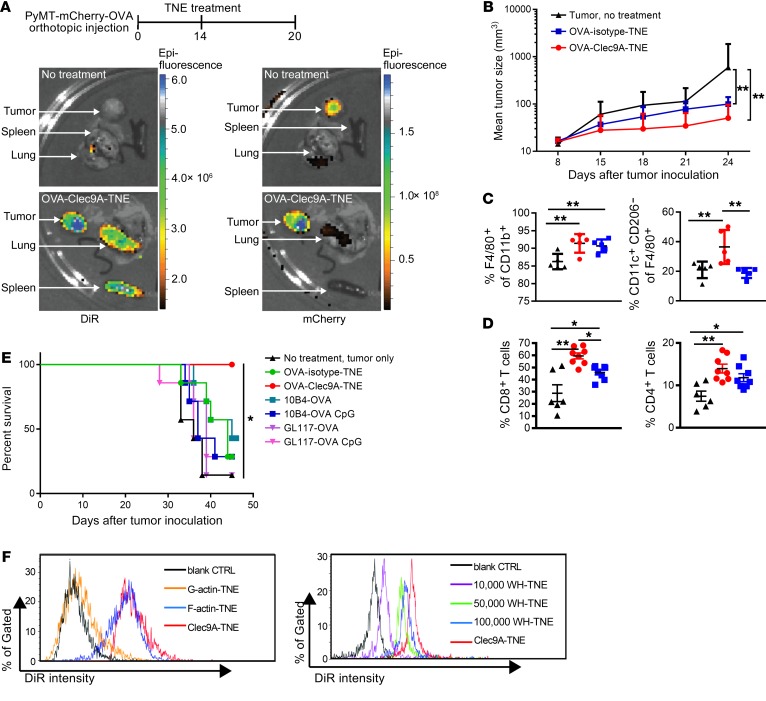
Figure 4. OVA-Clec9A-TNE target lymphoid organs and PyMT-mChOVA tumor and promote a proinflammatory tumor environment associated with tumor control.
(A) Organs were harvested from untreated or OVA-Clec9A-TNE–treated PyMT-mChOVA tumor–bearing mice. Images show distribution of DiR-labeled OVA-Clec9A-TNE in lung, tumor, and spleen, and colocalization with mCherry-expressing tumor. (B) C57BL/6 mice (n = 6–8) developing tumor after orthotopic injection of PyMT-mCherry-OVA were treated with OVA-Clec9A-TNE or OVA-isotype-TNE or left untreated. Mean tumor size is plotted over time for each group. (C and D) Percentages of M1-like CD11c+CD206– macrophages, total F4/80+CD11b+ macrophages (C), and CD8+ and CD4+ T cells (D) in tumor were analyzed by FACS, 6 days after TNE injection. (E) C57BL/6 mice (n = 7) inoculated with 106 AT3-OVA tumor cells and 10 days later injected i.v. once with OVA-TNE or OVA-mAb fusion conjugates with or without 10 μg CpG ODN 1668 CpG adjuvant, as indicated. Survival curves of tumor-bearing mice are shown. (F) C57BL/6 mice were injected i.v. with DiR-labeled G-actin–TNE, F-actin–TNE, or Clec9A-TNE (left panel) or 10,000 WH-TNE, 50,000 WH-TNE, 100,000 WH-TNE, and Clec9A-TNE (right panel); 16 hours later, splenocytes were fixed, and then DiR fluorescence intensity was analyzed, indicating uptake of DiR+ TNE by CD8+ cDCs. Representative of 4 mice per group. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 by 2-way ANOVA test. Survival analyses used the Mantel-Cox log-rank test.