Figure 3.
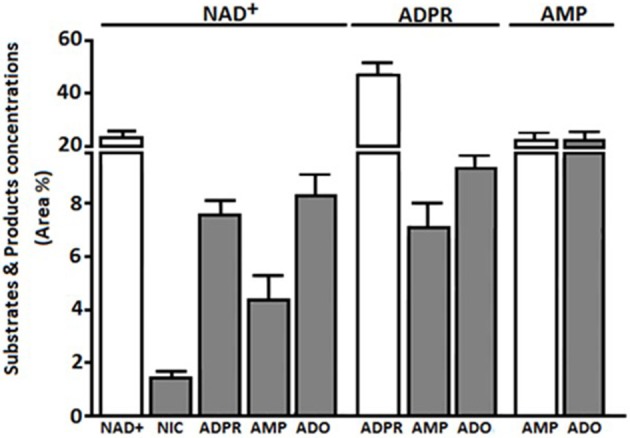
Extracellular products of CIK enzymatic reactions using NAD+, ADPR, and AMP as substrates. Products (NIC, ADPR, AMP, or ADO) obtained from bulk CIK cell cultures (n = 5) using (i) NAD+, (ii) ADPR or (iii) AMP as substrates, were evaluated by HPLC assays in the presence of the adenosine deaminase inhibitor (EHNA) as described in Materials and Methods. Products (gray bars) are expressed as area percentage (Area %) for each enzymatic product as compared to the total components present in the ACN-treated CIK cell supernatant (100%). Substrates are represented as Area % of consumed substrate (white bars). Results indicate that bulk CIK cells efficiently hydrolyze NAD+, ADPR and AMP to generate ADO. Of note, CIK cells produce low or undetectable amounts of ADO when incubated with NAD+, ADPR, or AMP substrates in the absence of EHNA (not shown). The identity of peaks was confirmed by the co-migration of reference standards.
