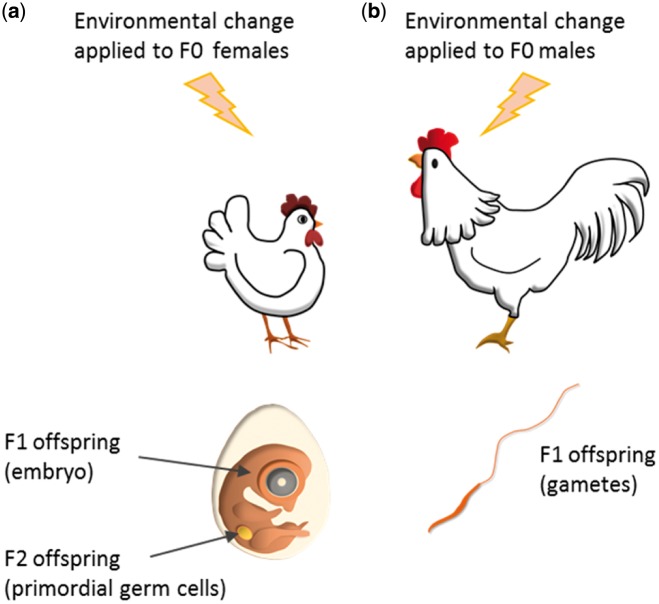
Figure 1:
The maternal environment directly impacts F1 and F2 offspring while the paternal environment only impacts F1 offspring. (a) A change in the maternal environment can affect egg components and thus may impact F1 individuals. However, as these F1 developing offspring bear the PGCs that will lead to differentiated gametes, the change in maternal environment may also impact F2 individuals. Thus only the effects observed on the F3 individuals will be considered as transgenerational effects. (b) A change in the paternal environment only affects its own gametes that will lead to the F1 generation. The effects observed on the F2 individuals will be considered as transgenerational effects