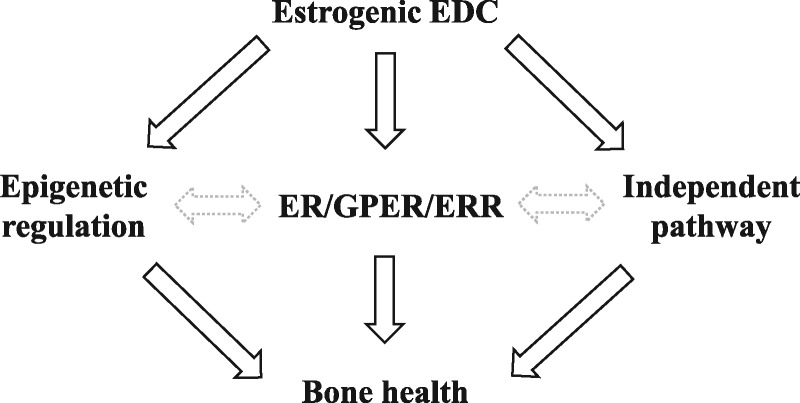
Figure 3:
proposed pathways of estrogenic EDC-induced skeletal health effects. While EDCs can act to disrupt epigenetic regulation, and have been shown to elicit effects through classical and nonclassical estrogen receptors, whether these effects are also found in bone remain to be determined. Moreover, the link between epigenetic regulation and ER/GPER/ERR signaling in bone are not well-defined. Given the pleiotropic effects of EDCs, direct and indirect pathways independent of epigenetics and hormone receptors could also affect bone health. Solid black lines: more established connections in the currently available literature. Gray dashed lines: Less established connections that remain to be explored. ER, estrogen receptor; GPER, G protein-coupled receptor; ERR, estrogen-related receptor.