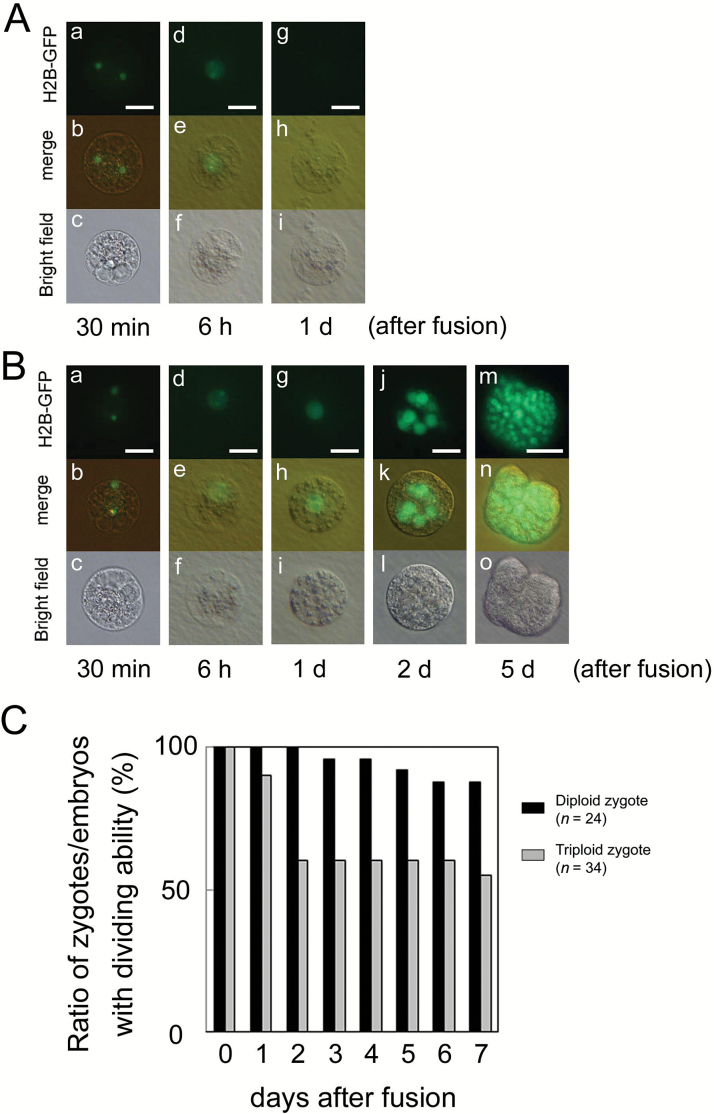
Fig. 4.
Developmental profiles of polyspermic triploid zygotes. An egg cell was serially fused with two sperm cells expressing H2B–GFP, and the resulting zygote was observed. (A) Failure of the first cell division in polyspermic zygote. Two sperm nuclei fluorescently labeled with H2B–GFP were observed in the fused egg cell (a–c). At 6 h after fusion, the H2B–GFP signal was detected in the zygotic nucleus, which was possibly derived from fusion of two sperm nuclei with an egg nucleus (d–f). However, the zygote did not divide at 1 d after fusion (g–i), and it degenerated thereafter. (B) In the polyspermic zygote, karyogamy was progressed to form a triploid zygotic nucleus (a–i), and the zygote further developed into a globular-like embryo at 2 d after fusion (j–l), and a cell mass (m–o). (C) Changes in rate of zygotes/embryos possessing dividing ability during culture of diploid zygotes (n=24) and polyspermic triploid zygotes (n=34). Upper, middle, and lower panels in (A, B) are fluorescence, merged fluorescence/bright-field, and bright-field images, respectively. Scale bars: 20 μm. (This figure is available in color at JXB online.)