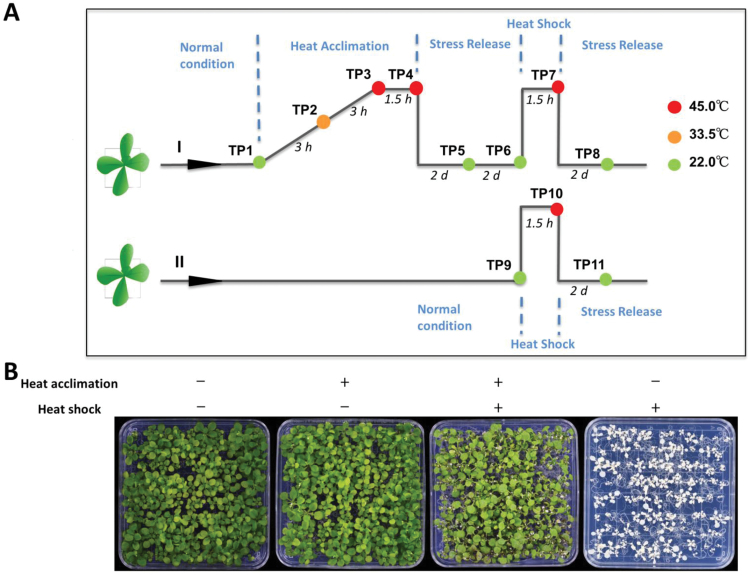
Fig. 1.
Outline of the platform used to induce heat-stress- priming. (A) Seedlings grown under long days were either primed (I) or not primed (II) with heat stress. During priming, the temperature was increased uniformly from 22 to 45 °C over 6 h, sustained at 45 °C for 1.5 h, and then brought down sharply to 22 °C. For the heat-shock process, the temperature was rapidly increased from 22 to 45 °C and then dropped down to 22 °C sharply after 1.5 h. The temperature of each sample collection time-point (TP) and the interval between the TPs are indicated. (B) Phenotypes of seedlings after different treatments. Pictures were taken when plants were 24 d old, 6 d after the heat shock.