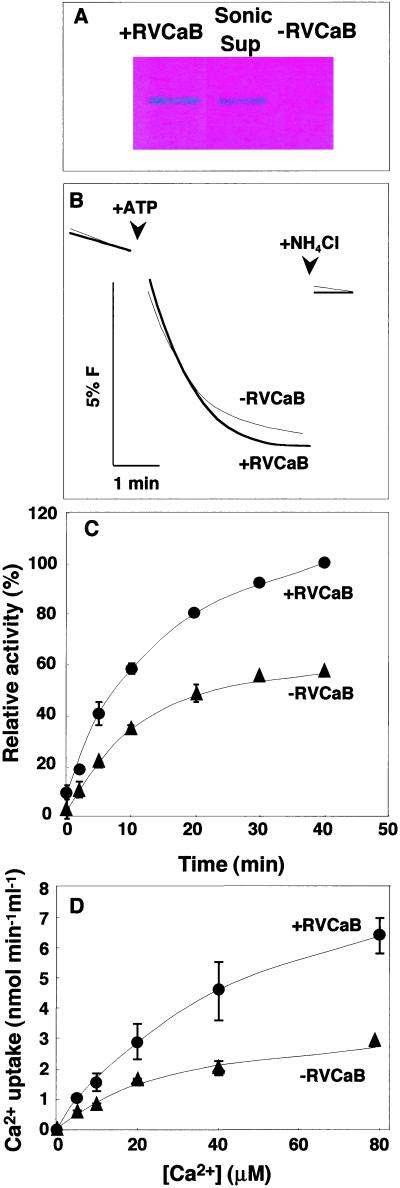
Figure 5.
RVCaB stimulates the Ca2+ uptake into vacuolar membrane vesicles. The vacuolar membrane vesicles with (+RVCaB) or without (−RVCaB) were prepared from radish taproots and then assayed for Ca2+ uptake activity. A, Detection of RVCaB. The membrane vesicles before (+RVCaB) and after sonication (−RVCaB) and the supernatant fraction after sonication (Sup) were subjected to SDS-PAGE and then the gel was stained with Stains-all. B, ATP-dependent H+ transport activity of the vesicles with (+RVCaB, thick line) and without RVCaB (−RVCaB, fine line) was measured as the rate of fluorescence (F) quenching of acridine. At the indicated time, NH4Cl was added at 1 mm to collapse a proton gradient. C, The Ca2+ uptake activity was assayed in a medium containing 100 μm CaCl2 (45Ca2+) by the filtration method. Black circles, +RVCaB; black triangles, −RVCaB. D, Vacuolar membrane vesicles with (+RVCaB, black circles) and without RVCaB (−RVCaB, black triangles) were assayed for Ca2+ uptake activity at indicated concentrations of CaCl2 for 2 min. The values correspond to the initial rates of Ca2+ uptake.