Figure 4.
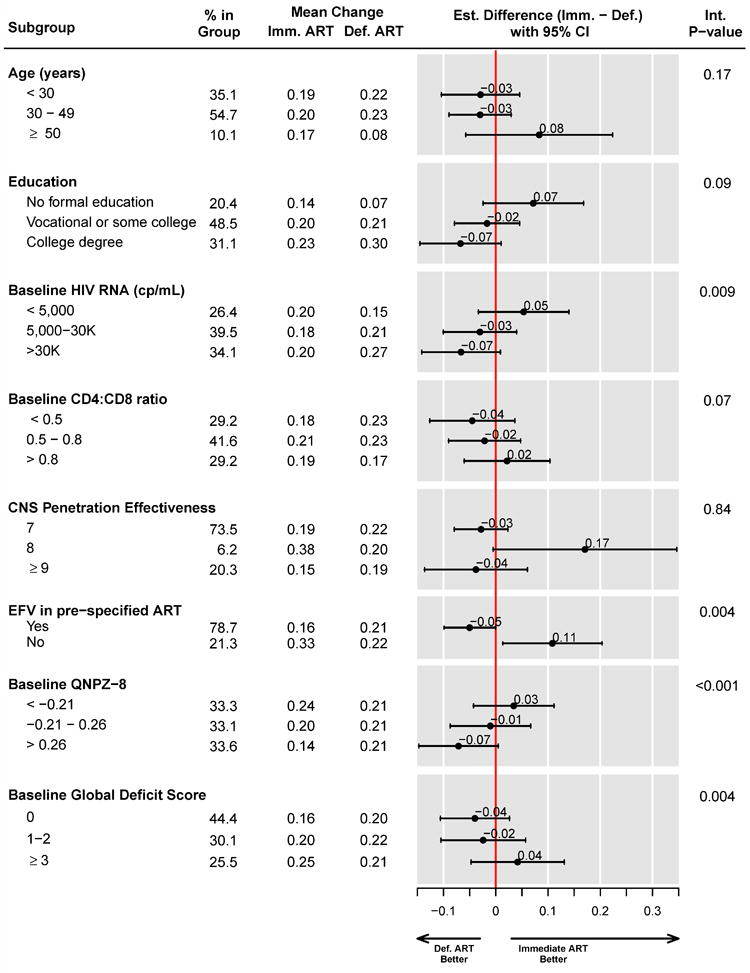
Subgroup analyses for change in mean QNPZ-8 scores from baseline.
When adjusting interaction p-values for multiple comparisons using the Benjamini-Hochberg false discovery rate (FDR) method, p≤0.004 provides evidence for heterogeneity of the treatment effect across subgroups at the FDR≤0.05 level. Subgroup analyses by age, education, HIV RNA level, pre-specified ART regimens, and their CNS penetration effectiveness score were specified a priori in the study protocol. In addition to the 8 subgroup factors shown, we analyzed subgroups by 16 baseline factors: by race, sex, employment status, urban residence, country of enrollment, time since HIV diagnosis, CD4 cell count, body mass index, diabetes, depression (CES-D≥16), prior psychiatric diagnosis, prior cardiovascular disease, 10-year Framingham risk of CHD, hematocrit, AST/SGOT, ALT/SGPT. The treatment effect was homogeneous across those 16 subgroups.
