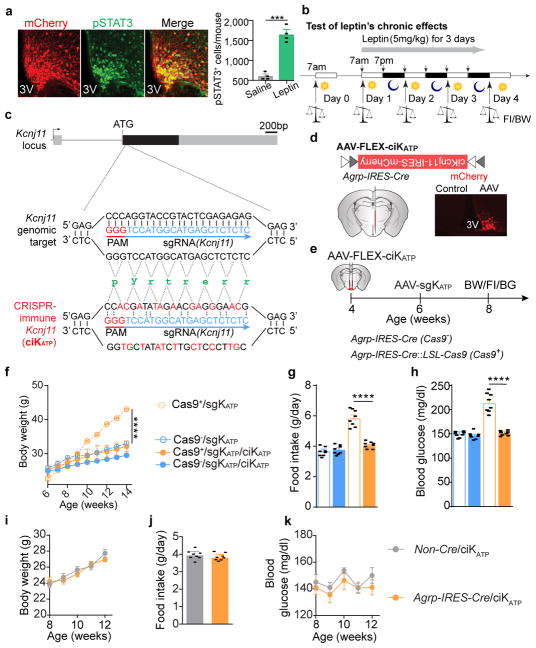
Extended Data Figure 6. Additional information on experimental design related to CRISPR-mediated deletion of Kcnj11 in AgRP neurons; Expression of a CRISPR-immune Kir6.2 in AgRP neurons prevents alterations in body weight, food intake, or blood glucose following CRISPR-mediated deletion.
a, Representative images and quantification of mCherry::pSTAT3 co-immunostaining (n=4 mice per group) following CRISPR-mediated disruption of Kcnj11 in AgRP neurons. b, Schematic diagram of experiment flow to test leptin’s chronic effects in regulating body weight and food intake. c, Diagram of sgRNA design targeting the mouse Kcnj11 locus and of CRISPR-immune Kcnj11 cDNA encoding the mouse KATP channel subunit Kir6.2 (ciKATP) with indicated silent mutations to prevent binding of sgRNA. d, Schematic diagram of Cre-dependent AAV pEF1α-FLEX-ciKcnj11-IRES-mCherry (AAV-FLEX-ciKATP) injected unilaterally into the ARC of Agrp-IRES-Cre::Leprdb/db mice and representative image of mCherry immunostaining. e–h, Diagram of experiment flow (e), body weight (f), daily food intake (g), and blood glucose measurements (h) in virus-transduced ad libitum fed littermates (n=8 mice per group). Expression of ciKATP in AgRP neurons completely prevented body weight gain, increased food intake and hyperglycemia induced by CRISPR-mediated deletion, suggesting that contributions from off-site mutagenesis are excluded. i–k, Body weight (i), food intake (j), and blood glucose (k) of Non-Cre and Agrp-IRES-Cre littermates following bilateral injection of AAV-FLEX-ciKATP into the ARC (n=8 mice per group), suggesting that AAV-mediated expression of ciKATP in AgRP neurons produces no obvious effects on energy or glucose balances. Data are mean ± s.e.m. and representative of three independent experiments; ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001; Student’s two-tailed, unpaired t-test (a, g, h, j) or two-way ANOVA analysis (f, i, k).