Fig. 2.
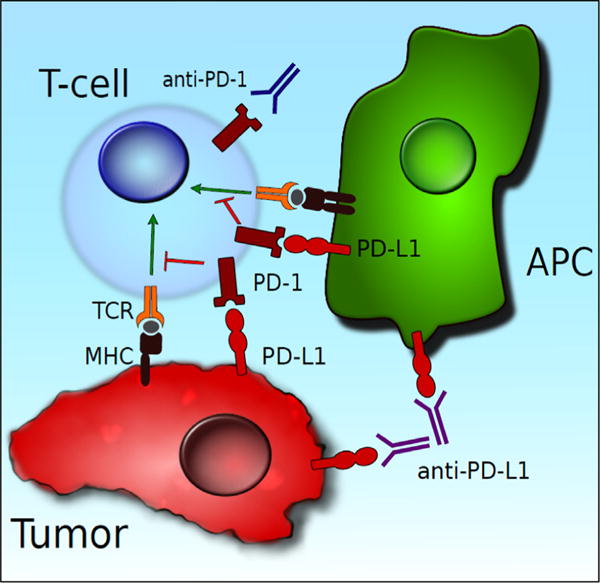
PD-L1 can be expressed on both APCs and tumor cells. PD-L1 binds to PD-1 on the T-cell surface, leading to coinhibition of T-cell activity. The PD-1/PD-L1 pathway can be blocked with anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies, leading to immune-mediated tumor destruction. (Color version of the figure available online.)
