Figure 1. Subfield labeling protocol.
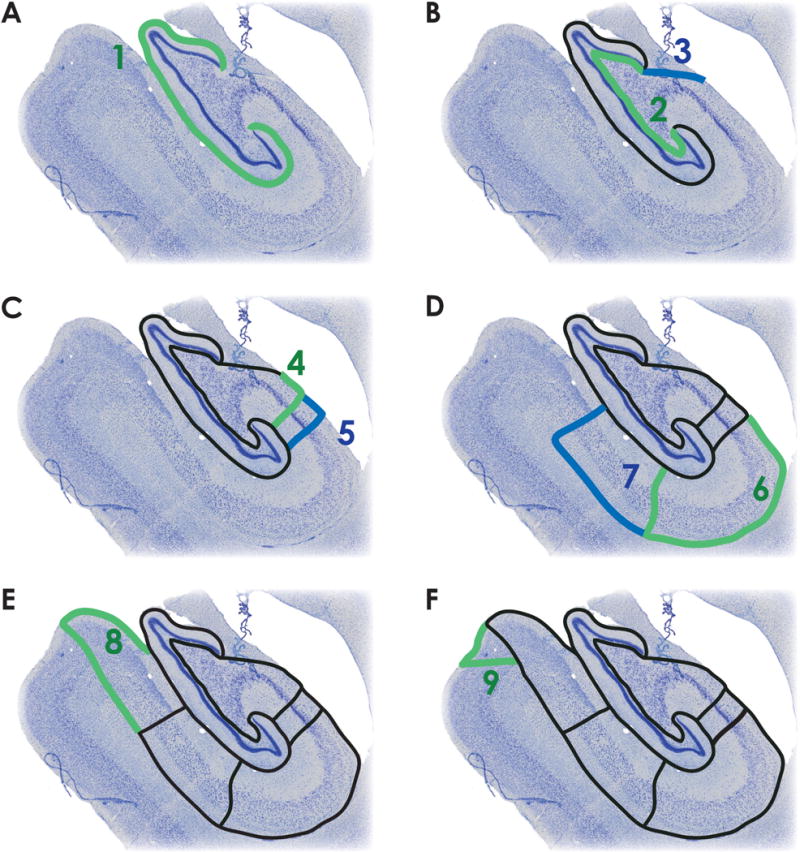
A. The outer boundary of the DG (dentate gyrus) is defined by the hippocampal fissure (green, step 1). B. The thin polymorphic layer, which lies adjacent to the granule cell layer (green, step 2), defines the inner boundary of DG. The fimbria is delineated from CA3 by connecting the medial blade of DG with alveus/lateral ventricle border (blue, step 3). C. The CA3/CA2 border is marked by the dense pyramidal cell layer of CA2, and is drawn parallel to the pyramidal cells of CA2/CA3 (green, step 4). The CA2/CA1 border is marked by a transition to the diffuse pyramidal cell layer of CA1 (blue, step 5). D. CA1 is defined by the alveus along the temporal horn of the lateral ventricle and along the alveus/ILF (inferior longitudinal fasciculus) border to the CA1/subiculum boundary, marked by a reduction in the presence of bipolar neurons and a change in the density and orientation of pyramidal cells (green, step 6). Subiculum is defined by the alveus/ILF border until the alveus boundary is lost. After the alveus, it’s approximate thickness is preserved relative to the cell layer. The subiculum/presubiculum boundary marked by the densely packed cells of the presubiculum (blue, step 7). E. The presubiculum is labeled by continuing along the ILF to the presubiculum/parasubiculum boundary, marked by a change in cell density (green, step 8). F. The parasubiculum/parahippocampal cortex boundary is marked by the transition to layered cortex. The cells of the parasubiculum are bound medially by laminar cortex and laterally by presubiculum (green, step 9).
