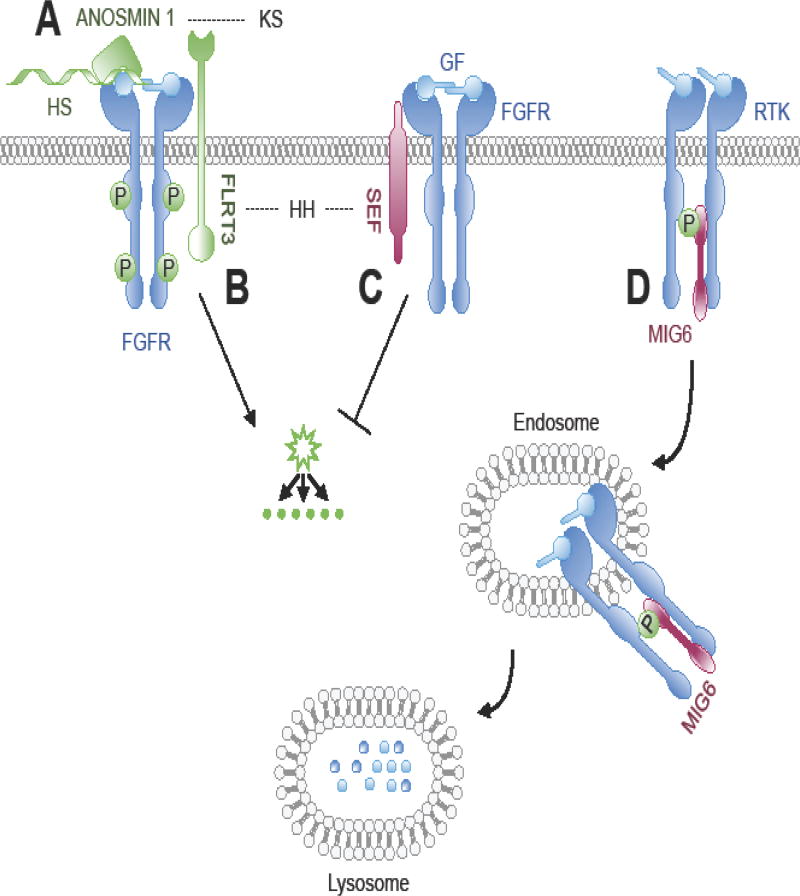
Figure 1. Modulation of RTK signaling by regulation of the ligand-receptor signaling complex formation.
(A) Heparin-bound Anosmin 1 binds to a pre-formed FGF2/FGFR1 complex, promoting its assembly and resulting receptor activation. FGFR signaling induces expression of FLRT3 and SEF via transcriptional activation and translation. (B) FLRT3 complexes with FGFR to promote downstream signaling of the MAPK/ERK pathway via its intracellular domain. (C) SEF complexes with FGFR and blocks receptor phosphorylation and activation of the RAS/MAPK and PI3K/AKT signaling cascades. (D) EGFR signaling induces MIG6 expression via transcriptional activation and translation. MIG6 accumulates in the cytoplasm where it binds directly with the ligand-activated ErbB kinase domain to inhibit auto-phosphorylation. This interaction can direct trafficking of the MIG-bound EGFR from the plasma membrane to late endosomes, targeting the receptor for lysosomal degradation. Dashed lines connecting the human congenital disorder with the protein in the pathway encoded by the causative mutated gene. Syndromes noted in the text and/or Supplemental Table 1. HH, hypogonadotropic hypogonadism with or without anosmia; KS, Kallmann syndrome; FGFR, Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor; GF, growth factor; HS, heparin-sulfate; P, phosphorylation; RTK, receptor tyrosine kinase.