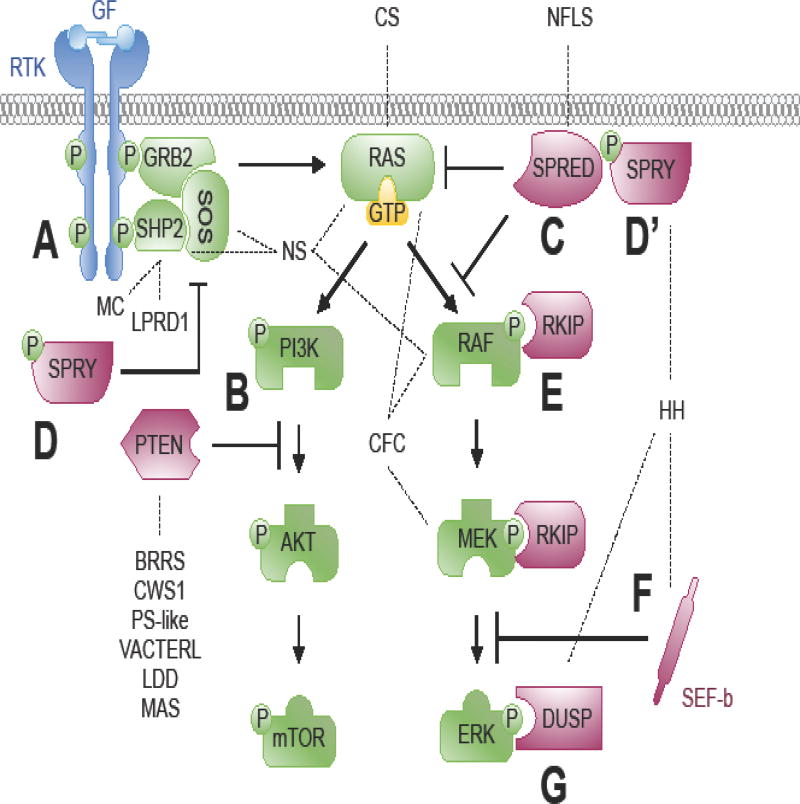
Figure 2. Feedback modulators of intracellular signal transduction cascades.
FGFR signaling induces expression of the SPRED family, the Sprouty family, SEF, and nuclear DUSPs via transcriptional activation and translation to attenuate RAS/MAPK signaling. (A) Growth factor-activated RTKs induce GRB2-mediated recruitment of SHP2 to signaling complexes. GRB2 redirects activated SHP2 to other signaling proteins that normally inhibit RTK signaling, subsequently acting as a positive regulator. (B) Growth factor-activated RTKs recruit and activate PI3K. The PI3K lipid signaling intermediate is dephosphorylated by PTEN, thereby attenuating PI3K/AKT signaling. (C) SPRED proteins increase RAF recruitment to the plasma membrane and prolongs RAS/RAF complexation, withdrawing RAF from activation by phosphorylation. (D, D’) Sprouty proteins translocate to the plasma membrane where they are phosphorylated. This phosphorylation induces a confirmation change that allows Sprouty proteins to bind and disrupt the GRB2/SOS complex, RAS activation, and RAF activation, thereby attenuating RAS/PI3K and RAS/MAPK signaling. (E) RKIP binds to both RAF1 and MEK to prevent their physical interaction and MEK phosphorylation, thereby attenuating RAS/MAPK signaling. (F) SEF-b suppresses activation at the level of, or downstream from, MEK. (G) DUSP6 dephosphorylates ERK. Dashed lines connecting the human congenital disorder with the protein in the pathway encoded by the causative mutated gene. Syndromes noted in the text and/or Supplemental Table 1. BRRS, Bannayan-Ruvalcaba-Riley syndrome; CFC, cardio-facio-cutaneous syndrome; CS, Costello syndrome; CWS1, Cowden syndrome 1; HH, hypogonadotropic hypogonadism with or without anosmia; LDD, Lhermitte-Duclos disease; LPRD1, LEOPARD syndrome 1; MAS, Macrocephaly/autism syndrome; MC, Metachondromatosis; NFLS, Neurofibromatosis Legius syndrome; NS, Noonan syndrome; PS-like, Proteus-like syndrome; VACTERL, vertebral anomalies, anal atresia, congenital cardiac disease, tracheoesophageal fistula, renal anomalies, radial dysplasia, and other limb defects; GF, growth factor; P, phosphorylation; RTK, receptor tyrosine kinase.