Fig. 1.
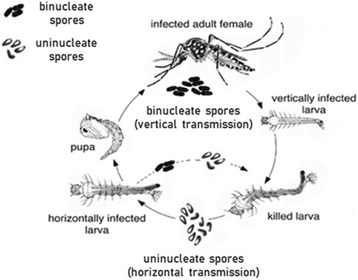
Life cycle of the microsporidia Edhazardia aedis infecting the mosquito Aedes aegypti. Usually (solid line), the parasite alternate vertical and horizontal transmission using two types of spores. Repeated horizontal transmission is possible (dashed line). Since the parasite’s life-cycle involves a strict alternation of binucleate and uninucleate spores, repeated horizontal transmission implies that the parasite goes through its complete developmental sequence – producing first binucleate and the uninucleate spores – within a juvenile mosquito. (Modified from [42])
