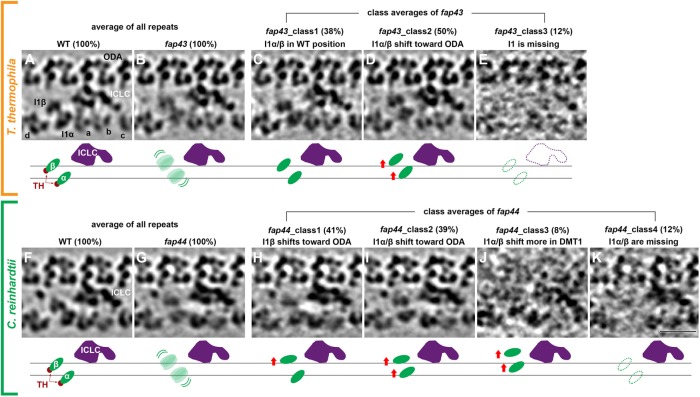
FIGURE 4:
Classification analyses reveal importance of T/TH complex for the structural/positional stability of the I1 dynein motor domains. (A–K) Tomographic slices (top) and schematic drawings (bottom) show the averages from all axonemal repeats (100%) from T. thermophila wild type (WT, A) and its fap43 mutant (B), as well as in C. reinhardtii wild type (WT, F) and its fap44 mutant (G). Note the relative weak and blurry appearance of the I1α and I1β motor domain densities in T.t. fap43 (B) and C.r. fap44 (G). Classification analyses focused on the I1 dynein motors of the axonemal repeats from T.t. fap43 (C–E) and C.r. fap44 (H–K) resulted in three and four classes, respectively. The key structural differences and the percentages of repeats included in each class are indicated. The horizontal black lines in the schematic drawings indicate the wild-type positions of the I1α/β motor domains (green). Other labels: a–d, inner dynein arm isoforms; ICLC (purple), intermediate and light chain complex; ODA, outer dynein arm. Scale bar: 20 nm.