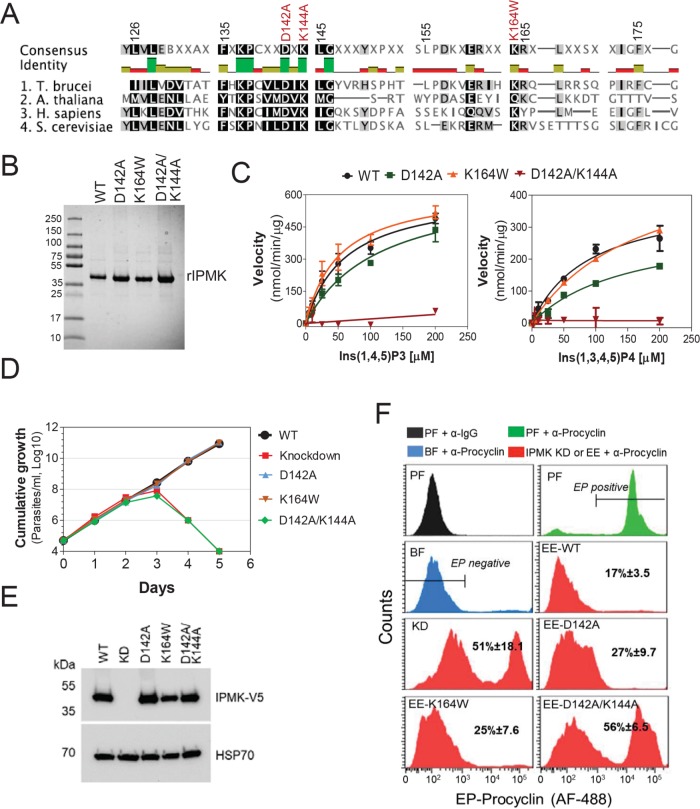
FIGURE 2:
Development of BFs to PFs depends on IPMK catalytic activity. (A) Alignment of catalytic sites of IPMKs of T. brucei, A. thaliana (gene ID: AED91147.1), Homo sapiens (gene ID: NP_689416.1), and Saccharomyces cerevisiae (gene ID: PJP09331.1). Mutated sites are shown in red. (B) Recombinant T. brucei IPMK WT or mutants (37 kDa) resolved on a 4–20% SDS–PAGE gel stained with Coomassie Imperial Staining (Pierce). (C) Activity analysis of rIPMK WT and mutants with Ins(1,4,5)P3 and Ins(1,3,4,5)P4 substrates. See Table 1 for kinetic parameters of each rIPMK enzyme and substrates. Growth curve (D) and Western blot analysis (E) of T. brucei IPMK CN exclusively expressing V5-tagged IPMK WT, mutants D142A, K164W, D142A/K144A, or no IPMK gene (knockdown). Cells were grown in the absence of tet for exclusive expression of introduced V5-tagged WT, mutant allele, or IPMK knockdown. Blots were stripped and reblotted with mAb 78, which recognizes mitochondrial HSP70. (F) Flow cytometry analysis and quantification of T. brucei expressing EP procyclin after IPMK knockdown or exclusive expression (EE) of WT or mutant IPMK alleles for 36 h in HMI-9 at 37°C in BF followed by 6 d in SDM-79 at 27°C.