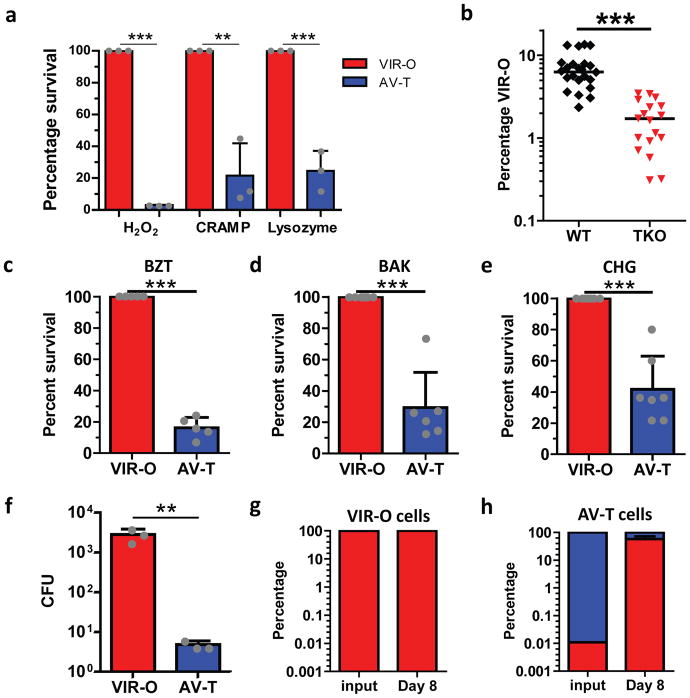
Figure 2. The host antimicrobial, hospital disinfectant and desiccation-resistant VIR-O cells are selected during in vivo infection.
(a), VIR-O (red) or AV-T (blue) were treated with H2O2, CRAMP or lysozyme, and percent survival relative to VIR-O was calculated. The reported values represent the mean of three replicates with standard deviations. Repeated experiments gave similar results. (b), Wild-type (WT, black) or triple knockout (TKO; red) mice lacking the gp91 subunit of the NADPH oxidase, lysozyme and CRAMP were infected with AV-T (n= 4 to 8/group). At 8 hours post-infection, lungs were harvested and plated to assess the percentage of VIR-O cells present. Presented data were pooled from three separate experiments and repeated at least 5 times for a total of 18–23 mice/per group. (c–e), VIR-O or AV-T was treated with the indicated amounts of disinfectants: (c) benzethonium chloride (BZT) 0.01%, (d) benzalkonium chloride (BAK) 0.004% and (e) chlorhexidine gluconate (CHG) 0.008%, and percent survival relative to VIR-O was calculated. Presented data were pooled from three separate experiments and a total of 5 replicates were used for (c), 6 replicates for (d) and 7 replicates for (e). (f–h), VIR-O and AV-T survival after desiccation. (f), Bacteria were rehydrated and plated on day 8 of desiccation to determine viability. Values represent the mean of three replicates. Recovered bacteria from the (g) VIR-O cells and (h) AV-T cells were assessed for the percentage of VIR-O and AV-T cells present. Error bars represent standard deviation of the mean and Student’s two-tailed t-test (**p < 0.005; ***p < 0.0005) in (a) and (c–h); Error bars represent geometric mean and a two-tailed Mann-Whitney test was to determine significance (***p < 0.0005) in (b).