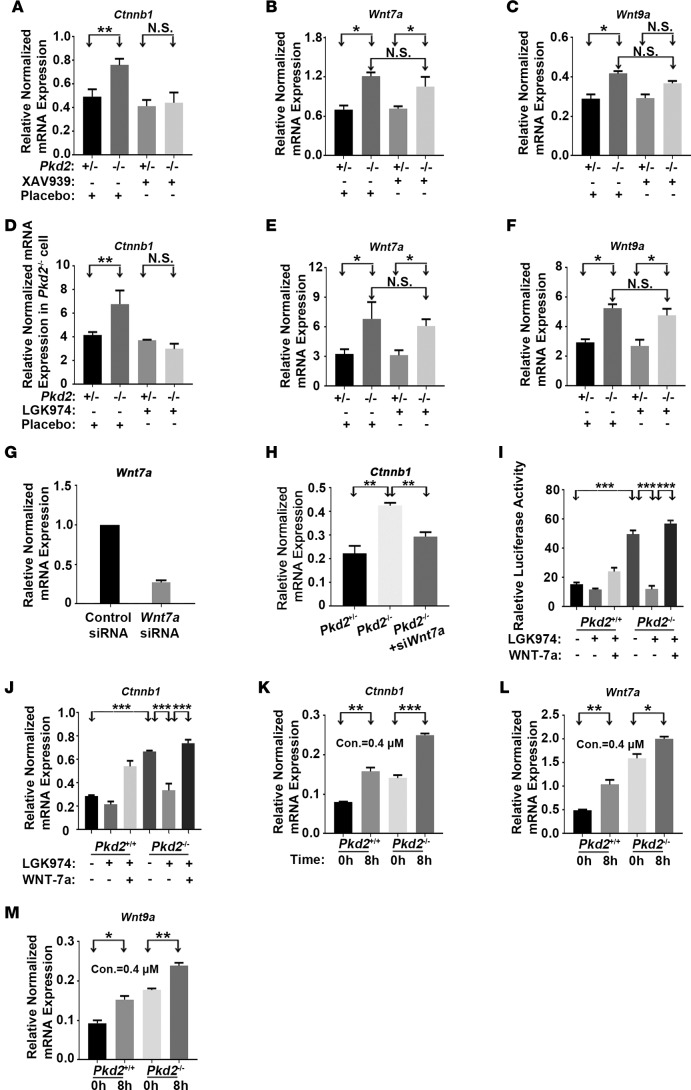
Figure 5. PC2 deficiency upregulates Ctnnb1, Wnt7a, and Wnt9a expression.
(A–C) XAV939 inhibited the PC2 deficiency–induced elevation of the mRNA levels of Ctnnb1 but not of Wnt7a or Wnt9a. Cells were treated with XAV939 (2 μM) for 16 hours, and mRNA levels were determined by quantitative RT-PCR. (D–F) LGK974 inhibited the Pkd2 deficiency–induced elevation of the mRNA levels of Ctnnb1 but not of Wnt7a or Wnt9a. Cells were treated with LGK974 (2 μM) for 24 hours, and mRNA levels were determined by quantitative RT-PCR. (G) Wnt7a mRNA levels in Pkd2−/− cells were measured 48 hours after Wnt7a siRNA treatment by quantitative RT-PCR. (H) Wnt7a knockdown reduced the Pkd2 deficiency–induced elevation of Ctnnb1 mRNA. (I) Luciferase reporter gene activity was elevated in Pkd2−/− cells. Cells were transfected with the luciferase reporter in the presence or absence of LGK974 (2 μM) and/or exogenously purified WNT-7a (100 nM/ml). Reporter gene activity was determined 24 hours after transfection. (J) Ctnnb1 mRNA levels were also measured in the presence or absence of LGK974 and/or exogenously purified WNT-7a by quantitative RT-PCR. (K–M) Intracellular calcium sequestration by BAPTA-AM increased Ctnnb1, Wnt7a, and Wnt9a expression. Cells were treated with the Ca2+ chelator BAPTA-AM (0.4 μM) for 8 hours. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, n = 3, Student’s t test).