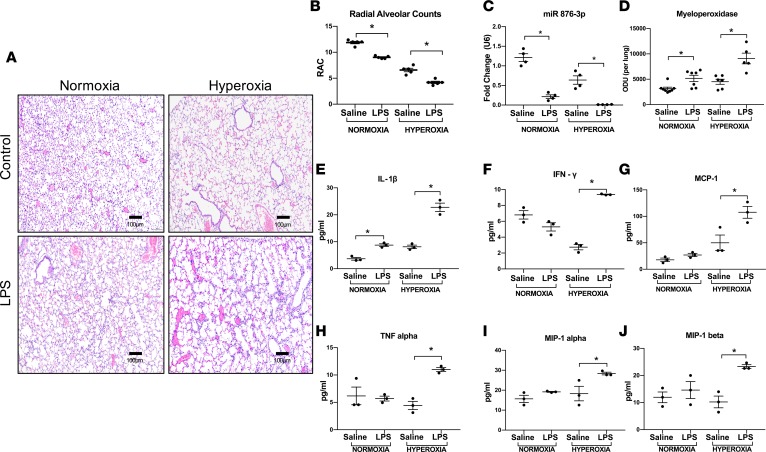
Figure 5. Postnatal Proteobacterial LPS decreases miR 876-3p expression in vivo.
We developed a double-hit model of BPD in which animals were exposed to postnatal LPS, in addition to hyperoxia exposure. (A and B) Addition of LPS was associated with more severe alveolar hypoplasia in both normoxia and hyperoxia. The RACs of both hyperoxia-treated pups and hyperoxia + LPS–treated pups were significantly lower than their respective air controls at P14. LPS alone, in normoxia, caused decreased alveolarization and potentiated the alveolar hypoplasia in hyperoxia. Magnification, 100×. (C) Exosomal miR 876-3p levels in BALF were reduced to a greater extent by LPS exposure in both normoxic and hyperoxic mice (C). (D) MPO activity was increased in LPS-exposed normoxic and hyperoxic mice compared with their respective controls (D). Hyperoxia + LPS–exposed mice showed increased inflammatory cytokines compared with: IL-1β (E), IFN-γ (F), monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP-1) (G), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α)(H), macrophage inflammatory protein–1α (MIP-1α) (I), and macrophage inflammatory protein 1 beta (MIP-1β) (J). *P < 0.05 by 1-way ANOVA. All in vivo experiments were conducted with n = 5–7 animals per group.