Figure 8. MsrB3-immunoreactivity in the hippocampal white matter arteriolar walls changes in Alzheimer’s disease.
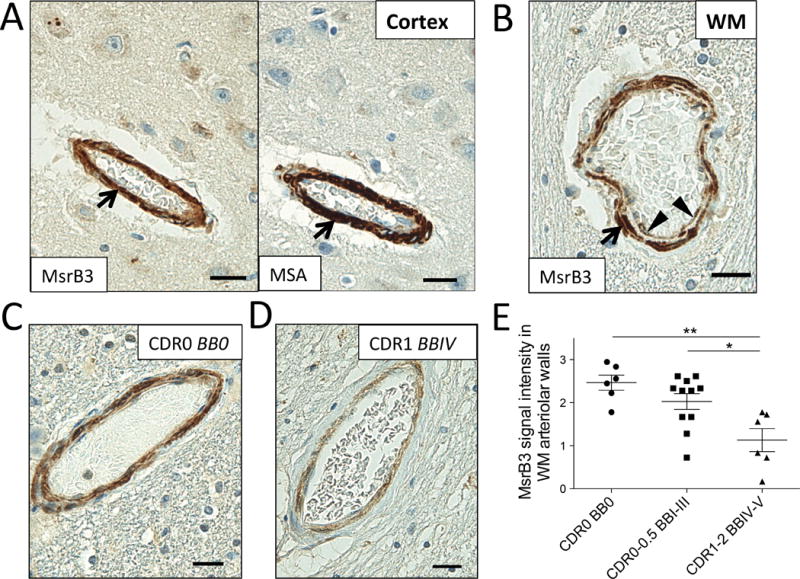
MsrB3 was strongly expressed in smooth muscle of vessel walls (arrows), highlighted in adjacent section with muscle-specific actin (MSA) IHC, in hippocampal cortex (A) and white matter (WM) (B). (B) An arteriole in hippocampal WM shows MsrB3 immunoreactivity in smooth muscle (arrow) and endothelial/pericyte (arrowheads) cell layers. Hippocampal WM arteriolar walls were strongly MsrB3-immunoreactive in healthy controls (CDR0, BB0) (C), while weak signal was often found in AD subjects (CDR1, BBIV) (D). (E) The intensity of MsrB3 signal in the arteriolar walls of hippocampal white matter was significantly reduced in AD patients compared to controls and subjects with early AD-associated pathology. Scale bars = 20 μm. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, by one-way ANOVA.
