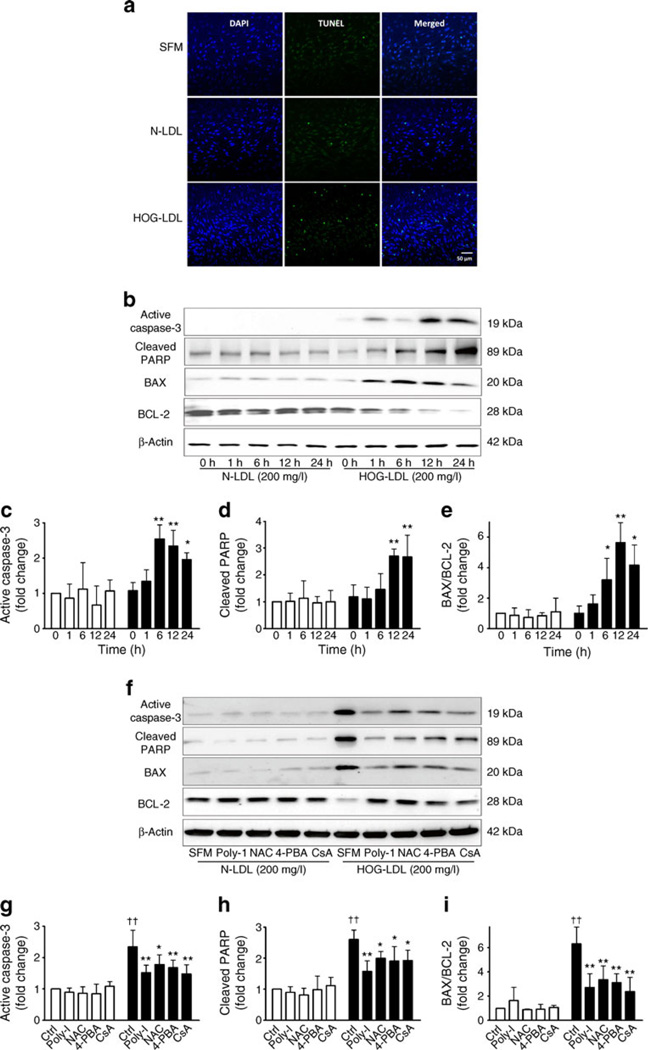
Fig. 5.
HOG-LDL induces apoptosis in HRCP. (a) TUNEL staining in HRCP. Apoptotic cells were observed by TUNEL assay when HRCP were exposed to HOG-LDL (200 mg/l) vs N-LDL (200 mg/l) for 24 h. Apoptosis significantly increased after HOG-LDL, but not after N-LDL treatment. Images are representative of three independent experiments. (b) Time course of activated caspase-3, cleaved PARP, BAX and BCL-2 in HRCP. Cells were treated as above (Fig. 2b) and western blot experiments performed on total protein extracts, with β-actin used as loading control. (c) Quantification of findings for activated caspase-3, (d) cleaved PARP and (e) BAX and BCL-2, expressed as means ± SD; n=3; *p<0.05 and **p<0.01 vs HOG-LDL 0 h. White bars, N-LDL; black bars, HOG-LDL. (f) Poly-I, NAC, 4-PBA and CsA inhibit HOG-LDL-induced apoptosis in HRCP. Cells were treated for 24 h as shown and protein levels as indicated detected by western blot. (g) Quantification of findings for activated caspase-3, (h) cleaved PARP and (i) BAX: BCL-2 ratio, expressed as means ± SD; n=3; *p<0.05 and **p<0.01 vs HOG-LDL control; ††p<0.01 vs N-LDL control