Fig 2.
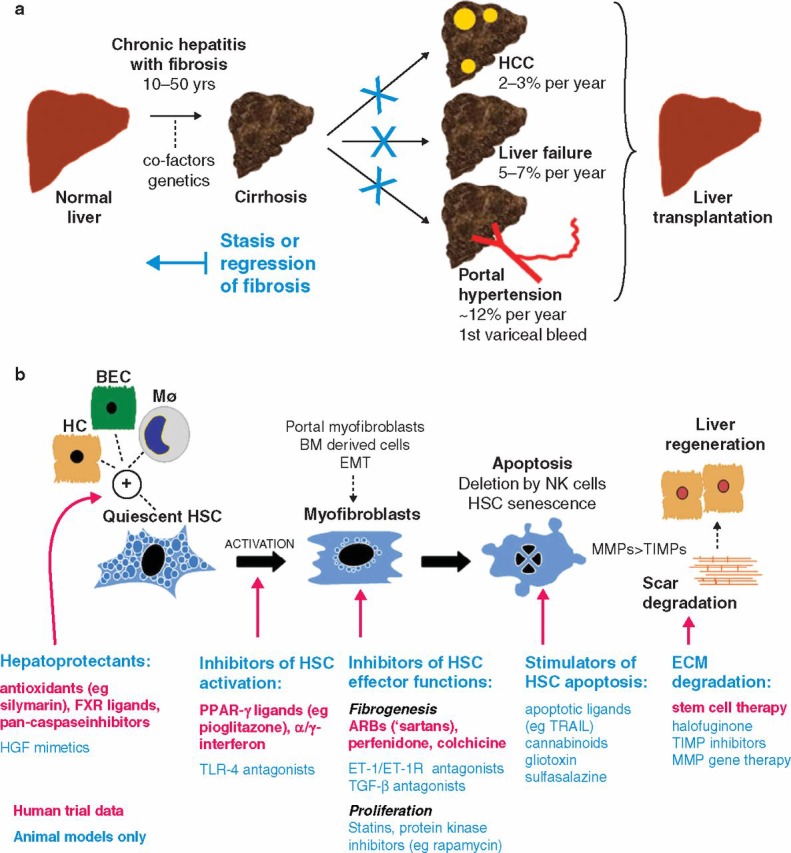
Antifibrotic therapy in human liver disease: (a) natural history of liver fibrosis and the potential role of antifibrotic therapy. Stasis or regression of fibrosis could reduce the complications of cirrhosis and obviate the need for liver transplantation; (b) illustrated summary of emerging therapies for liver fibrosis that target critical pathways of fibrogenesis and fibrolysis. ARB = angiotensin-11 type-1 receptor blocker; BEC = biliary epithelial cell; BM = bone marrow; ECM = extracellular matrix; EMT = epithelial to mesenchymal transition; ET-1(R) = endothelin-1(receptor); FXR = farnesoid X receptor; HC = hepatocyte; HCC = hepatocellular carcinoma; HSC = hepatic stellate cell; Mϕ = macrophage; MMP = metalloproteinase; NK = natural killer cell; PPAR = peroxisomal proliferator activated receptor; TGF = transforming growth factor; TIMP = tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase; TLR = toll-like receptor; TRAIL = tumour necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand.
