Fig. 1. MCS growth in hydrogel ECMs.
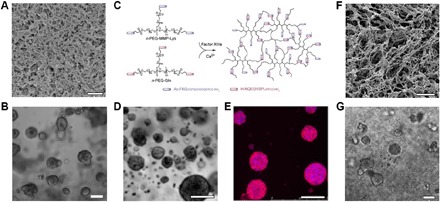
(A) Scanning electron microscopy image of Matrigel. Scale bar, 1 μm. (B) Phase-contrast microscopy image of MCSs grown from MCF-7 breast cancer cell lines in Matrigel for 14 days. Scale bar, 100 μm. (C) PEG hydrogels are formed by a transglutaminase Factor XIIIa–catalyzed cross-linking reaction between two multi-arm PEG-peptide conjugates: n-PEG-MMP-Lys and n-PEG-Gln. Phase-contrast microscopy (D) and confocal microscopy (E) images of MCSs grown from OV-MZ-6 ovarian cancer cell lines in PEG hydrogels shown in (C). Scale bars, 100 μm. Cell actin filaments were stained with rhodamine phalloidin (red), and the nuclei were stained with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI; blue). (F) Scanning electron microscopy image of the hydrogel formed from poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)–modified CNCs. Scale bar, 10 μm. (G) MCS growth from MCF-7 breast cancer cell lines in hydrogels shown in (F). Scale bar, 100 μm. Figures were reproduced with permission from Poincloux et al. (44) (A), Ehrbar et al. (66) (C), Loessner et al. (64) (D and E), and Li et al. (14) (F and G).
