Figure 5. Cardiolipin Synthesis Is Required for MCSR Induction, and Inhibiting Ceramide Synthesis Resulted in MCSR Induction.
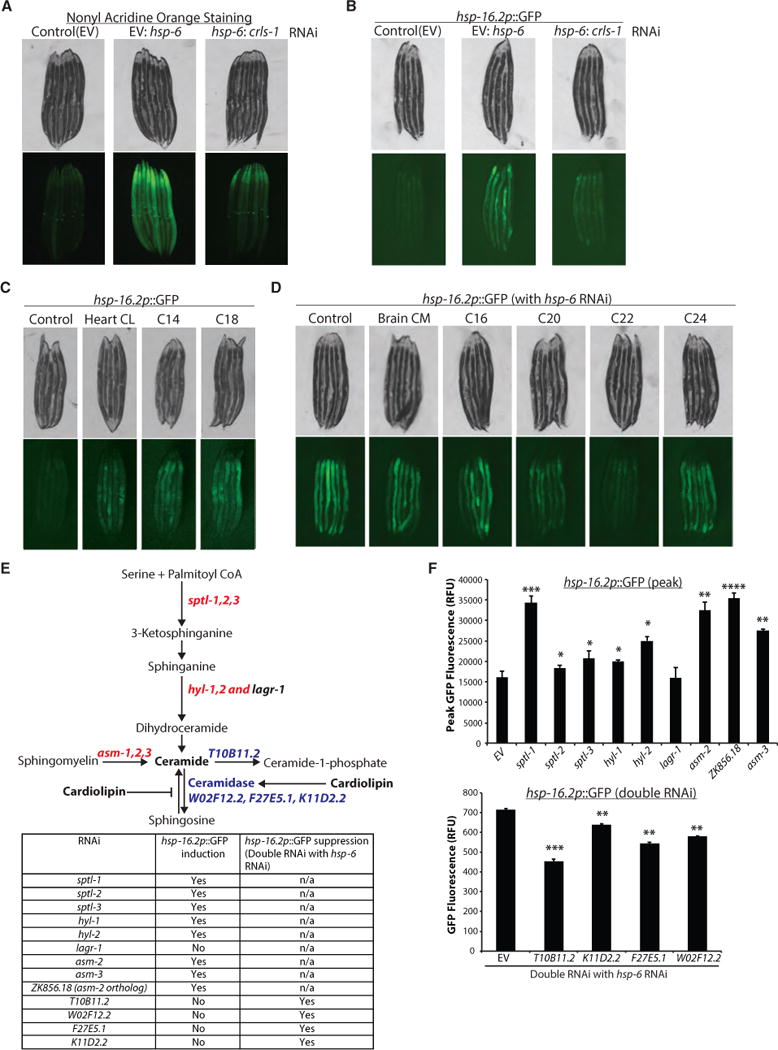
(A) Nonyl acridine orange staining showed that hsp-6 RNAi induced cardiolipin accumulation, while cardiolipin synthase (crls-1) RNAi in addition to hsp-6 RNAi blocked cardiolipin accumulation in wild-type worms.
(B) hsp-16.2p::GFP induction upon hsp-6 RNAi was inhibited by crls-1 RNAi.
(C) Cardiolipin-fed hsp-16.2p::GFP reporter worms showed increased GFP signal. Control, 0.5% methanol; Heart CL, cardiolipin purified from the bovine heart; C14, C14:0 cardiolipin; C18, C18:1 cardiolipin.
(D) Ceramide-fed hsp-16.2p::GFP reporter worms showed inhibition of MCSR upon hsp-6 RNAi. Control, 0.5% methanol; Brain CM, ceramide purified from the porcine brain; C16, C16 ceramide; C20, C20 ceramide; C22, C22 ceramide; C24, C24 ceramide.
(E) Diagram of the ceramide synthesis pathway. RNAi of enzymes written in red induced hsp-16.2 reporter, and RNAi of enzymes written in blue reduced MCSR induction. List of enzymes that were knocked down and the RNAi result are summarized in the table.
(F) Quantification of hsp-16.2p::GFP reporter induction and suppression (mean ± SD of three biological repeats; *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001, ****p ≤ 0.0001). hsp-16.2p::GFP reporter induction in the top panel shows the peak GFP signals from the individual worms, and the hsp-16.2p::GFP reporter suppression in the bottom panel shows the suppression of an hsp-6 RNAi-induced MCSR (double RNAi was applied at a one-to-one ratio).
See also Figure S5 and Table S3.
