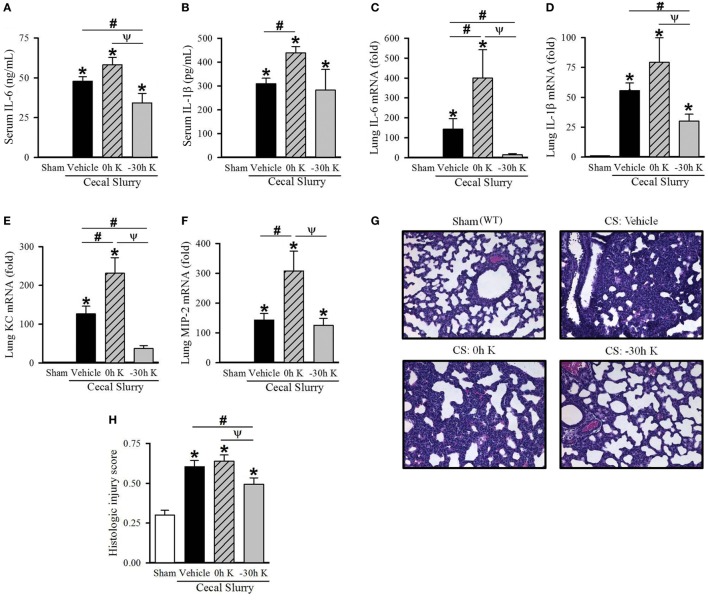
Figure 1.
Effect of KRN treatment timing on inflammation and pulmonary injury in septic neonatal mice. Neonatal C57BL/6 pups received KRN (0.2 µg/g BW) or vehicle (2.5% dimethyl sulfoxide in PBS) intraperitoneal (i.p.) within 1 h after (0 h K) or 30 h prior to (−30 h K) sepsis induction. Sepsis was induced by i.p. injection of cecal slurry (0.9 mg/g BW); serum and lungs were harvested 10 h later. Serum levels of (A) IL-6 and (B) IL-1β were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The mRNA levels of (C) IL-6, (D) IL-1β, (E) KC, and (F) MIP-2 in the lungs were determined by qPCR. (G) Shown are representative hematoxylin and eosin-stained sections of the lung from sham, vehicle-treated, 0 h KRN-treated and −30 h KRN-treated animals at 200× magnification. (H) Histologic lung injury score was calculated for each group, with a maximum possible score of 1. Data expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 6–8 per group) and compared by one-way analysis of variance (*p < 0.05 vs. Sham, #p < 0.05 vs. Vehicle, Ψp < 0.05 vs. 0 h K).