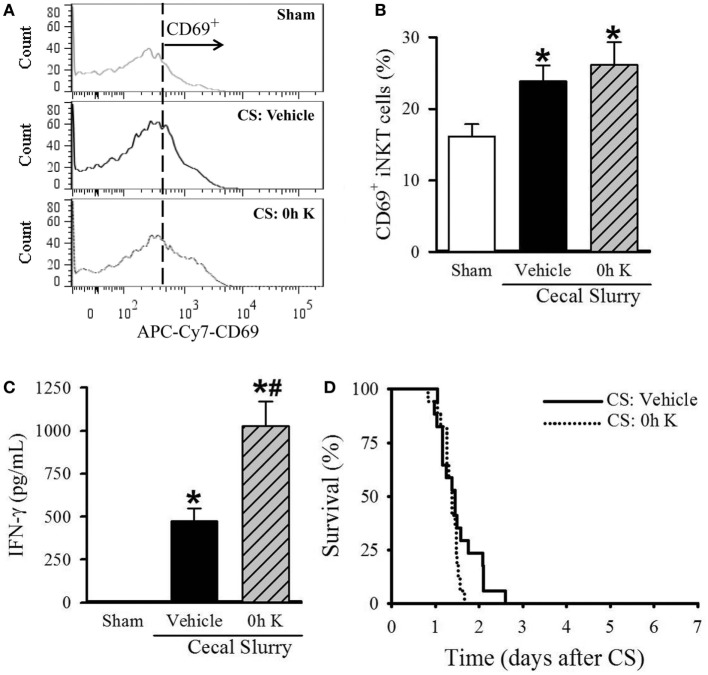
Figure 3.
Effect of 0 h KRN treatment on invariant natural killer T (iNKT) cell activation and survival in septic neonatal mice. Sepsis was induced in neonatal C57BL/6 pups by intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection of cecal slurry (CS, 0.9 mg/g BW). Pups then received KRN (0.2 µg/g BW) or vehicle (2.5% dimethyl sulfoxide in PBS) i.p. within 1 h. Serum and liver were harvested 10 h later. (A) Representative histogram of CD69 expression on hepatic iNKT cells. (B) Flow cytometric analysis of surface CD69 expression on gated hepatic iNKT cells. (C) Interferon (IFN)-γ levels in the serum were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Data expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 6–9 per group) and compared by one-way analysis of variance (*p < 0.05 vs. Sham, #p < 0.05 vs. Vehicle). (D) Another set of pups received the same dose of KRN or vehicle within 1 h after sepsis induction by CS (0.175 mg/g BW) and survival was monitored for seven days (n = 17 per group, p = 0.129, log-rank test).