Fig. 6.
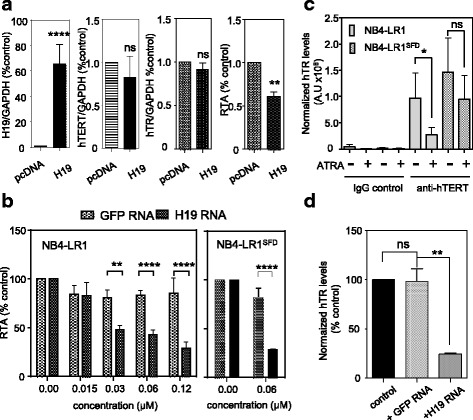
H19 RNA inhibits telomerase activity by altering the assembled telomerase complex. a Influence of H19 overexpression on hTR and hTERT expression and telomerase activity. NB4 cells were submitted to nucleofection in the presence of H19 (H19-pcDNA) or empty vector (pcDNA). Six hours after nucleofection, proteins and RNA were extracted. The levels of H19, hTR RNA, and hTERT mRNA were quantified by qRT-PCR and normalized to the levels of GAPDH mRNA. RTA was measured by qTRAP. b In vitro concentration-dependent inhibition of telomerase activity by H19. NB4-LR1 cells were extracted with CHAPS buffer. In vitro transcribed H19 was incubated with protein extracts for 90 min. Before assessment of telomerase activity. In vitro transcribed GFP was included as a specificity control. RTA measured by qTRAP is expressed as the percentage of that detected in protein extracts not supplemented with RNA molecules. c Lysates prepared from NB4-LR1 and NB4-LR1SFD cells treated or not with ATRA (1 μM) for 48 h were subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) with IgG or anti-hTERT antibodies. The immunoprecipitates were extracted for hTR analysis by quantitative RT-PCR. d Lysates from non-treated NB4-LR1 cells were preincubated with in vitro transcribed H19 RNA molecules subjected to IP using the hTERT antibody. The immunoprecipitates were then incubated for 90 min. Co-precipitated RNA were extracted and hTR assembled with hTERT quantified by qRT-PCR. As a control, an in vitro transcribed GFP RNA was used. Results were expressed as means +/− SEM. t-test or two way ANOVA *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001
