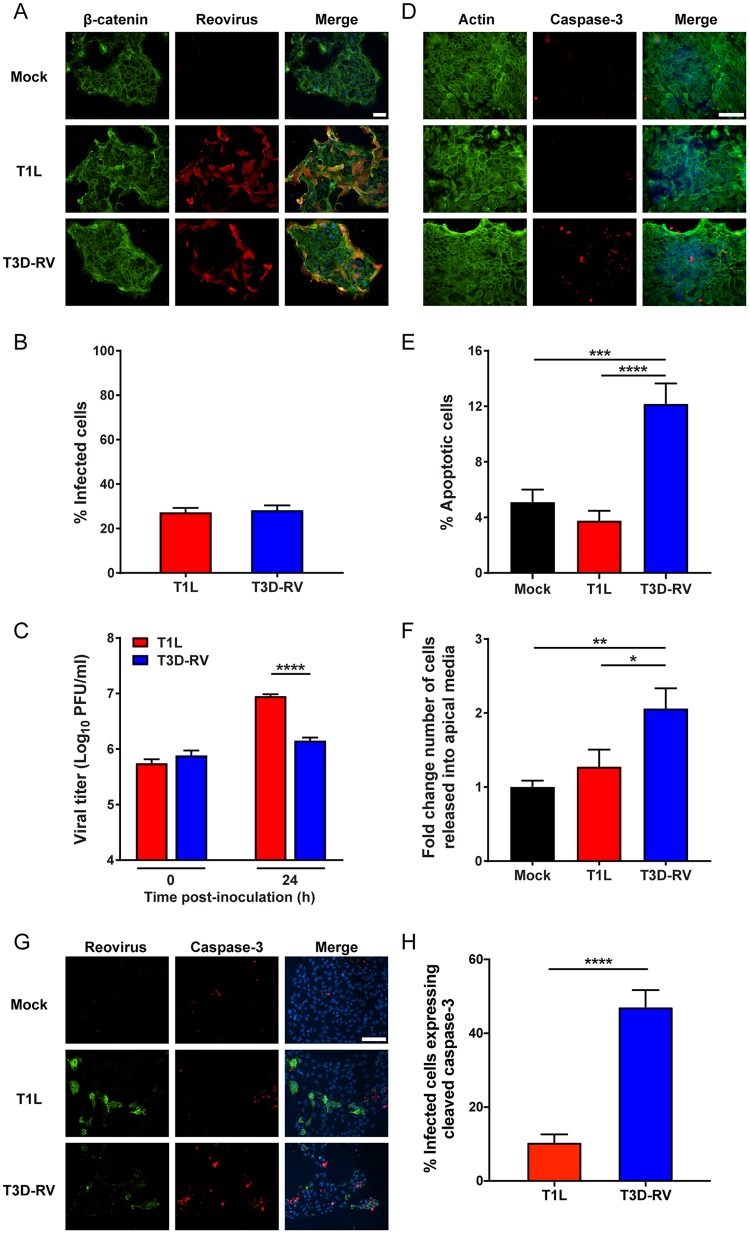
FIG 3.
Viral infectivity and apoptosis in murine-derived enteroids following reovirus T1L and T3D-RV infection. Intestinal crypts were harvested from mice and established as enteroids in Matrigel. The enteroids were dissociated, seeded onto Transwell plates, and incubated at 37°C for 4 days. Enteroids were adsorbed with T1L or T3D-RV at an MOI of 100 PFU/cell or with PBS as a mock control. At 24 hpi, cells were fixed and stained with antibodies specific for β-catenin and reovirus polyclonal antiserum (A and B) or actin and cleaved caspase-3 (D and E). Nuclei were labeled with ProLong Gold antifade mountant containing DAPI (scale bar, 50 μm). (B) The percentage of infected cells was determined by enumeration of reovirus-positive cells from immunofluorescence images. (C) Viral titers were determined at the intervals shown by plaque assay and expressed as PFU per milliliter of cell homogenate. (E) The percentage of apoptotic cells was determined using the Nikon Elements Basic Research analysis software and represents the number of cleaved caspase-3-positive cells per total number of cells in the selected field. (F) The number of cells released into the apical medium was quantified using an automated cell counter. (G and H) At 24 hpi, cells were fixed and stained with an antibody specific for cleaved caspase-3 and a polyclonal antiserum specific for reovirus nonstructural protein μNS. Nuclei were labeled with ProLong Gold antifade mountant containing DAPI (scale bar, 50 μm). (H) The percentage of infected cells expressing cleaved caspase-3 was determined by dividing the number of costained reovirus-positive and cleaved-caspase-3-positive cells by the number of reovirus-positive cells and then multiplying the quotient by 100. Data represent results from two to four independent experiments performed in triplicate. Error bars indicate SEMs. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001. P values were determined by Mann-Whitney test (C and H) and one-way ANOVA and Tukey's multiple-comparison test (E and F).