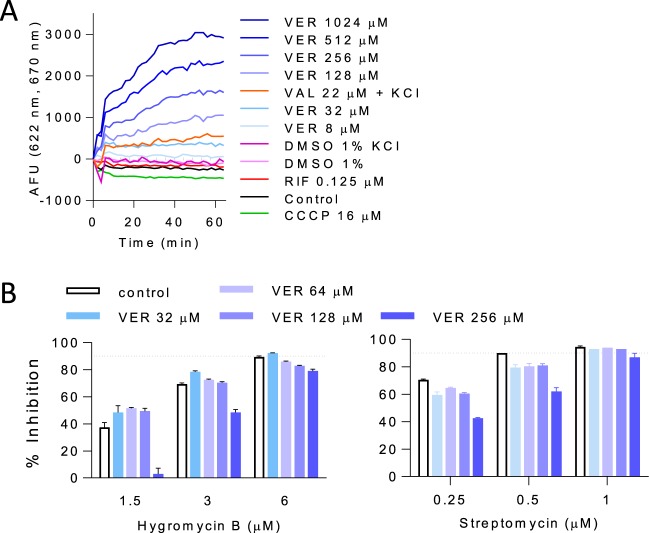
FIG 4.
Effect of verapamil on membrane functions. (A) Dose-response effect of verapamil on M. tuberculosis membrane electric potential. Membrane depolarization was measured using the membrane potential-sensitive fluorescent DiSC3 dye (5), which concentrates in energized membranes such that high local concentrations lead to decreased fluorescence intensity due to quenching. Upon dissipation of the membrane potential, the dye is released in the extracellular space, resulting in increased fluorescence. VER, verapamil; VAL, valinomycin; RIF, rifampin; CCCP, carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenyl hydrazine; AFU, arbitrary fluorescence units. (B) Effect of verapamil on the inhibitory activity of the aminoglycosides hygromycin B and streptomycin. The MIC of hygromycin B and that of streptomycin in the absence of verapamil were 6 and 0.5 μM, respectively.