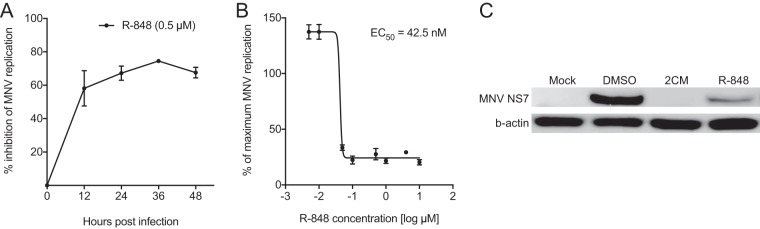
FIG 2.
R-848 displays potent inhibition of MNV genome replication and protein synthesis. For all panels, RAW264.7 infections were performed with an MOI of 0.05, and cells were incubated for 48 h. R-848 was tested at 0.5 μM unless otherwise stated. All calculations were performed relative to mock control, i.e., 0.05% (vol/vol) DMSO. (A) The inhibitory effect of R-848 on MNV replication was determined by quantification of viral genomes at 12-h intervals by RT-qPCR. Inhibition increased over time with a maximum level of inhibition (75.7%) recorded at 36 hpi. (B) To determine the EC50 of R-848 against MNV at the replication level, viral genomes were again quantified by RT-qPCR following incubation with eight different concentrations of R-848 and results were compared to those obtained in an uninhibited DMSO control (5 nM to 10 μM). R-848 treatment resulted in an EC50 of 42.5 nM. (C) To illustrate the inhibition of viral protein synthesis by R-848, the levels of MNV polymerase (NS7) were detected by Western blotting of lysates from infected cells. The nucleoside inhibitor 2′CM (10 μM) was used as a positive control, and the level of b-actin was also probed in samples for normalization. Inhibition of MNV protein synthesis is evident from the decreased band intensity observed with R-848 treatment. Graphed data in panels A and B show the means ± SEM for two independent experiments performed in either triplicate (panel A and C) or quadruplicate (panel B) reactions.