FIG 3.
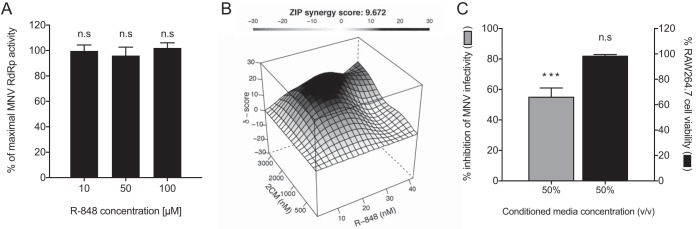
R-848 is synergistic with the nucleoside analogue 2′CM and induces cellular secretion of antiviral molecules. Several assays were performed to further probe the antiviral nature of TLR7 agonists. (A) First, the effect of R-848 on the in vitro transcriptional activity of the MNV RdRp was measured using a quantitative fluorescent assay. R-848 was tested at 10, 50, and 100 μM, and transcriptional activity was compared to that in mock-treated samples (DMSO). No effect on RdRp activity was observed with the addition of R-848. (B) The combined inhibitory effects of the TLR7 agonist R-848 (0 to 40 nM) and the nucleotide inhibitor 2′CM (0 to 3 μM) were tested over a range of combinations against MNV in cell culture using the plaque reduction assay. A dose-response matrix was generated and analyzed for synergism using SynergyFinder. The ZIP mode synergy score is presented as the average of all δ-scores across the dose-response landscape, and a δ-score of >0 indicates synergism. 2′CM and R-848 display a synergistic antiviral effect against MNV. (C) To determine if R-848-treated cells produce soluble antiviral molecules, CM from R-848-treated cells was screened for anti-MNV activity using the plaque reduction assay. CM used at a final concentration of 50% (vol/vol) displayed >50% inhibition of MNV with an absence of cytotoxic effects. Data were analyzed using an unpaired t test. n.s (not significant), P > 0.05; *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001. All data shown are the means ± SEM from three independent experiments with either duplicate (panel B) or triplicate (panels A and C) reactions.