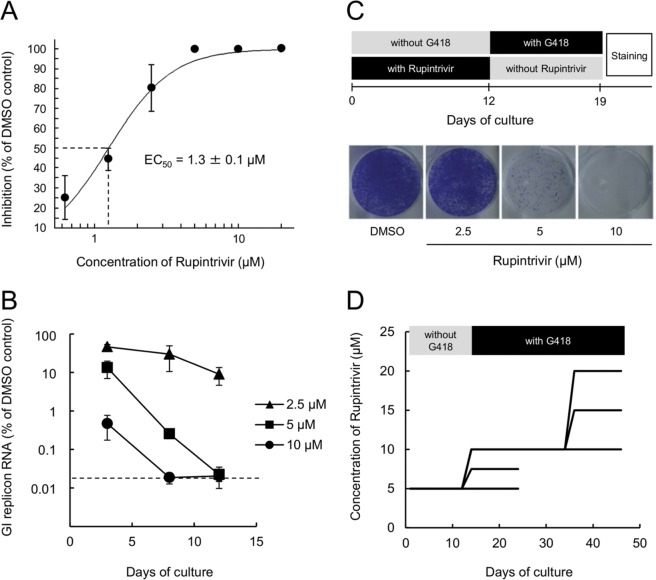
FIG 1.
Isolation of rupintrivir-resistant HGT-NV replicon cells. (A) Dose-response curve of effect of rupintrivir on HuNoV replicon RNA levels in HGT-NV cells. The level of replicon RNA in HTG-NV cells treated with DMSO or rupintrivir was measured by quantitative RT-PCR. Inhibition was plotted as a percentage relative to that in DMSO-treated cells. Error bars represent means ± standard deviations from three independent experiments. (B) Reduction in the GI replicon RNA level over time in HGT-NV cells treated with rupintrivir in the absence of G418. The levels of HuNoV replicon RNA relative to those observed in control DMSO-treated cells were plotted. Error bars represent means ± standard deviations from three biological replicates. Dashed line, detection limit for replicon RNA. (C) Colony formation assays with HGT-NV cells treated with DMSO or rupintrivir for 12 days. Colonies were stained and photographed on day 7 after treatment with G418 (1.5 mg/ml) in the absence of rupintrivir. (D) Schematic overview of the procedure used for the repetitive cultivation of HGT-NV cells in the presence of increasing concentrations of rupintrivir. HGT-NV cells were maintained as subconfluent cultures in the presence of DMSO or rupintrivir and G418 and passaged every 2 to 3 days for 45 days.