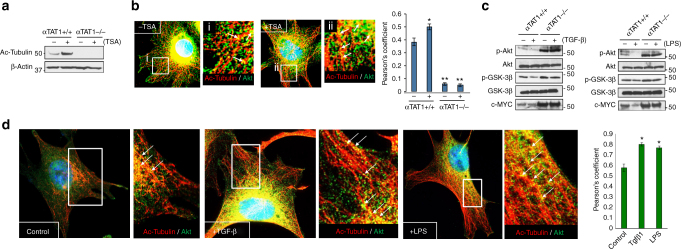
Fig. 6.
MT acetylation inhibits AKT activation. a Western blot analyses demonstrating acetyl tubulin level post Trichostatin A (TSA; 500 nM) treatment for 30 min in αTAT1+/+ and αTAT1–/– MEFs. b αTAT1+/+ and αTAT1–/– MEFs were treated with 500 nM of TSA for 30 min before fixing and immunofluorescence staining for acetyl tubulin (red) and total Akt (green). Representative images are obtained from αTAT1+/+ MEFs with and without TSA treatment. Acetyl tubulin levels were undetectable in αTAT1–/– cells. Pearson’s correlation coefficient was calculated to determine the proximity between acetyl tubulin and total Akt. Image J plugin called Just another co-localization plugin (JACoP) was used to quantify the images. Thirty cells per condition and three ROIs per cell were quantified. Error bars represent SEM and type 2 t-test analysis show relative to αTAT1+/+ control: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.0001. c αTAT1+/+ and αTAT1–/– MEFs were treated with TGF-β1 (200 pM; 30 min) or LPS (10 ng/ml; 30 min) before western blot analyses of the lysates for levels of pAKT S473, total AKT, pGSK3β, total GSK3β, and c-MYC. d Immunofluorescence images demonstrating localization of acetyl tubulin (red) and total Akt (green) in αTAT1+/+ MEFs post treatment with TGF-β1 (200 pM; 30 min) or LPS (10 ng/ml; 30 min). Pearson’s correlation coefficient was calculated using JACoP, 15 cells per condition, and 3 ROIs per cell were quantified. Error bars represent SEM and type 2 t-test analysis show relative to αTAT1+/+ control: *p < 0.05