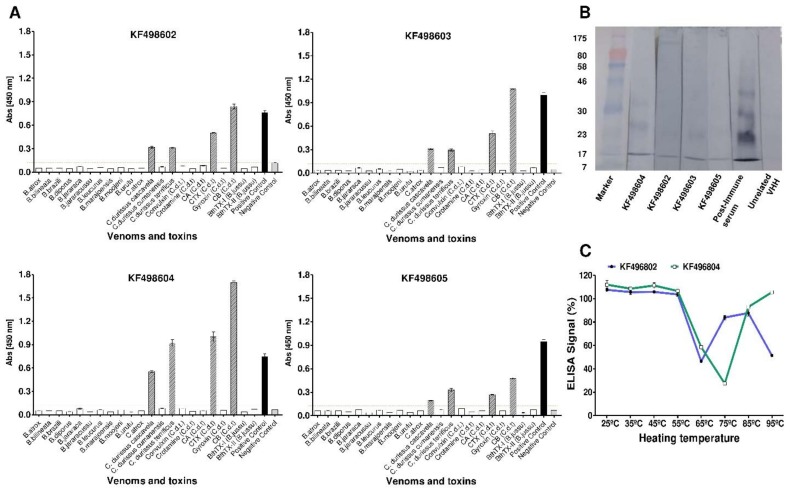
Figure 2.
Evaluation of VHHs’ specificity and thermostability. (A) cross-reactivity of anti-crotoxin VHHs. In vitro reactivity showing different levels of interaction of selected VHHs KF498602; KF498604; KF498605; KF498606 with snake venoms and isolated toxins. Absorbance obtained by ELISA assays performed on plates coated with 10 µg/mL of each antigen and VHH at a ratio of 1:1 (w/w). The dashed lines represent the cut off. All measurements were performed in triplicate. For the negative control (NC), unrelated VHH was used in wells coated with CTX. Each value represents the mean ± SEM of triplicate samples; (B) specificity analysis of the VHHs with CB by Western blot. Immunoblotting demonstrating the interaction of the selected clones with monomeric (14 kDa) and multimeric forms of CB on a nitrocellulose membrane; (C) VHHs’ functional thermostability using ELISA. Signal percentage in ELISA against CB of KF496802 (blue) and KF496804 (green), after heating from 25 to 95 °C for 1 h, compared to the pre-heating samples. Each value represents the mean ± SEM of triplicate samples.