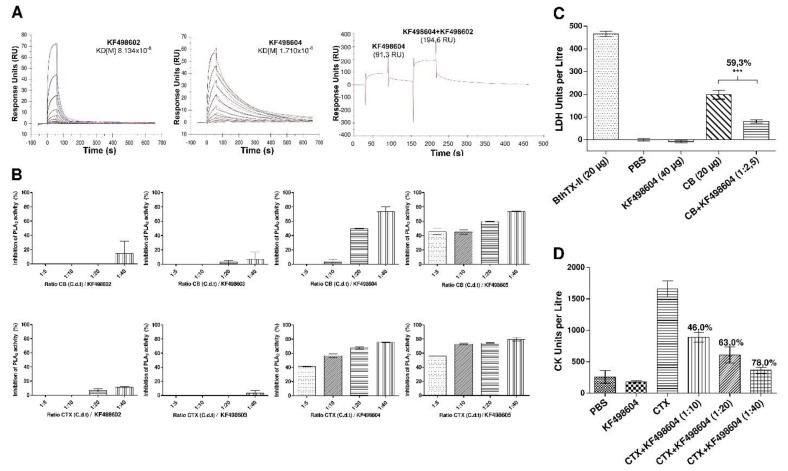
Figure 3.
Evaluation of VHHs’ kinetic interaction and neutralization ability. (A) analysis of the kinetic interaction between VHHs and CTX by SPR. Sensorgrams obtained after injection of KF498604 and KF498602, at concentrations from 2.5 to 0.002 μM, on a crotoxin-coated CM5 chip. KD = affinity constant of the clones. Sensorgram obtained after injection of KF498604 and co-injection of KF498602. Signal gain (103 RU) on the sensorchip surface after KF498602 injection indicates that these clones interact with different epitopes of crotoxin; (B) in vitro inhibition of CB and CTX phospholipase activity by selected VHHs. Fluorimetric analysis of inhibition was assayed using synthetic fluorescent phospholipids and toxins pre-incubated with selected VHHs for 30 min at 37 °C in different proportions (1:5; 1:10 and 1:40 w/w). The toxin’s activity on the phospholipids, in the absence of VHH, was used as a positive control, and considered as having 100% activity. The negative controls were carried out using medium reactions with no toxins. Each value represents the mean ± SEM of duplicate samples; (C) inhibition of CB-induced cytotoxicity in murine C2C12 skeletal muscle myotubes by VHH. Cytotoxicity (cytolysis) was estimated by the release of lactic dehydrogenase (LDH) into the culture medium after 3 h of exposure to a pre-incubated solution containing CB and the KF498604 at a 1:2.5 (w/w) ratio. A significant reduction in LDL release was observed in cells exposed to the solution containing CB and VHH (59.3%, *** p < 0.05), when compared to samples incubated with CB alone; (D) in vivo neutralization of CTX-induced myotoxicity by VHH. Myotoxicity was estimated by plasma creatine kinase (CK) levels in Swiss mice after 3 h of intramuscular administration of the pre-incubated preparations (37 °C for 1 h) containing CTX and KF498604 VHH in proportions of 1:10, 1:20 and 1:40 (w/w). The negative control was performed with PBS or VHH, and as a positive control, animals were injected with CTX with no VHH addition. Each value represents the mean ± SEM. Bonferroni’s test was used to measure significance. A significant reduction in CK levels was observed in the plasma of mice exposed to CTX and VHH in all proportions (1:10 = 46%; 1:20 = 63%; 1:40 = 78%, *** p < 0.05) in relation to those exposed to the toxin alone.