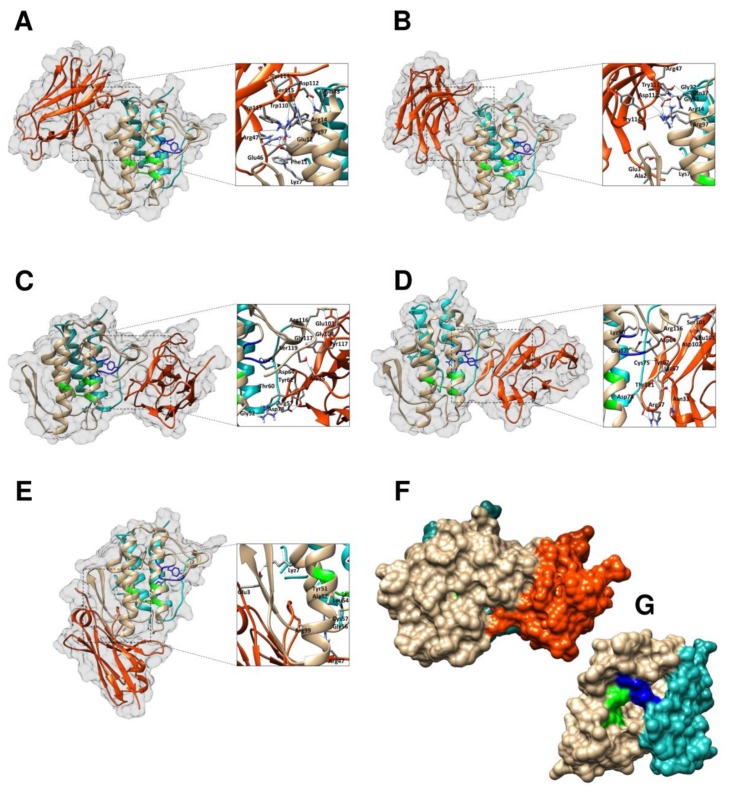
Figure 4.
Docking results showing VHH binding sites on the surface of crotoxin, isoform CA2CBb. Cartoon representations of VHH-CTX interaction structures (side view) covered by a white surface, where α, β and γ chains of CA are shown in cyan ribbon, CB in light brown and the VHH is shown as an orange ribbon. The active site of CB (His48, Asp49, Tyr53 and Asp99) is represented in green and the Ca2+ binding loop (Try28, Cys29, Gly30, Trp31, Gly32) in blue. (A) KF498602-CTX; (B) KF498603-CTX; (C) KF498604-CTX; (D) KF498605-CTX; (E) KF498606-CTX; (F) surface representation of the KF498604–CTX interaction (side view); (G) surface representation of crotoxin’s crystal structure (front view, PDB ID 3R0L). Interaction sites were enlarged in order to show hydrogen bonds formed between amino acid residues. While the clones KF498602 and KF498603 recognize CB from a region opposite from the catalytic site (N-terminal α-helix A and α-helix D, mainly), KF498604 and KF498605 interact with the CA-CB interface of crotoxin, and, despite no contact with the catalytic site (His48, Asp49, Tyr53 and Asp99), sterically block the access of the substrate as demonstrated in (C,D,F). KF498605 VHH also interacts with CA in a region opposite from CB’s catalytic site.