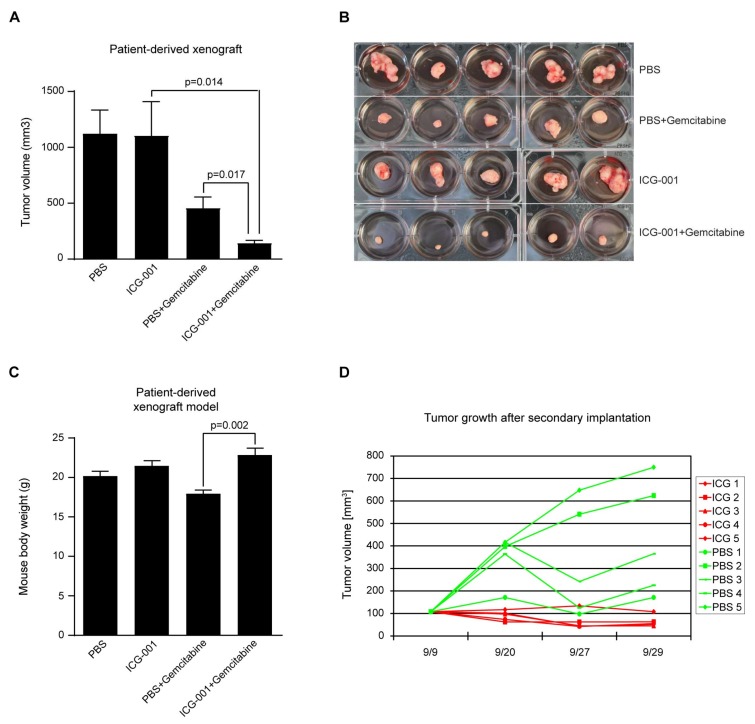
Figure 5.
Combination ICG-001 and gemcitabine treatment suppresses human patient-derived PDAC in a mouse xenograft model; ICG-001 effectively targets tumor-initiating cells. (A–C) Patient-derived PDAC was implanted subcutaneously into the flanks of immunocompromised NOD/SCID/IL2rγ−/− mice. Two weeks after primary implantation, treatment was initiated with 4 groups, i.e., saline control, ICG-001 50 mg/kg/day s.c., gemcitabine 100 mg/kg/day twice a week i.p., or the combination. Treatment was continued for 3 weeks at which point mice were sacrificed and tumors examined. Whereas ICG-001 alone failed to slow growth of tumors, gemcitabine alone significantly slowed tumor growth. However, combination of ICG-001 plus gemcitabine most dramatically decreased tumor growth as evidenced by tumor volume and visual inspection (A,B). ICG-001 ameliorated gemcitabine toxicity as judged by increased body mass among mice in the combination treatment group versus the gemcitabine-only treatment group (C). n = 5. (D) After secondary implantation of human PDAC was performed without any further treatment, tumors previously subjected to ICG-001 treatment (during primary implantation) failed to grow, whereas tumors previously subjected to phosphate buffered saline (PBS) treatment grew similarly to the first implantation, indicating that ICG-001 targets tumor-initiating cells. n = 5.