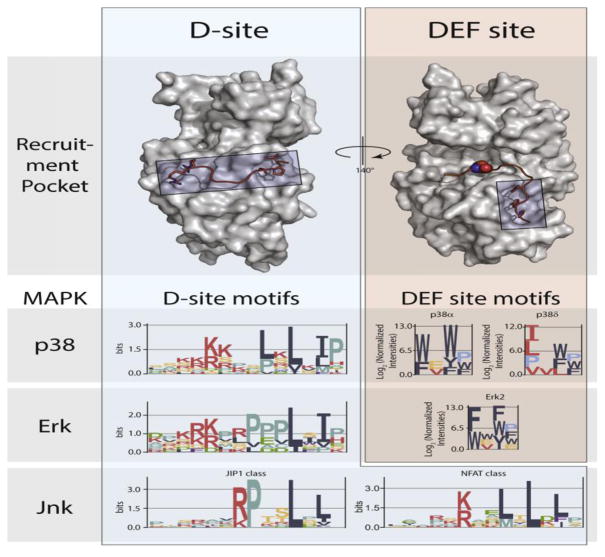
Figure 3.
MAPK docking interactions. Substrate D-site motifs (left) bind to a groove located on the opposite face of the kinase from the catalytic cleft. D-sites contain a cluster of basic residues upstream of two or three hydrophobic residues, the spacing of which can select for distinct MAPKs. ERK and p38 MAPKs can also bind DEF-sites (right) through a pocket adjacent to the active site, with different isozymes targeting distinct motifs. Logos for D-sites and DEF-sites were generated from published data [20, 25], using EnoLogos. ERK2 structures (top) were based on the co-crystal structure with the HePTP D-site peptide (PDB: 2FYS) and an HDX-MS model of a bound DEF-site peptide [21].