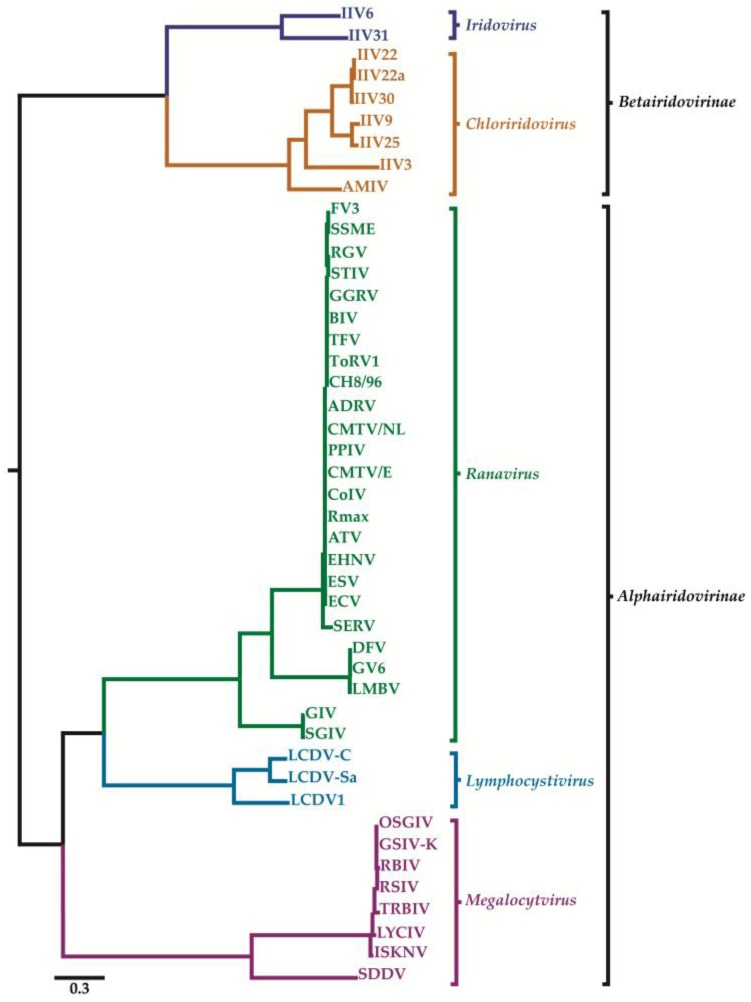
Figure 2.
ML analysis based on 26 core genes conserved among all members of the family Iridoviridae (iridovirids). The phylogram shows a clear division of genera within the Alphairidovirinae (Ranavirus, green; Lymphocystivirus, cyan; Megalocytivirus, purple) and Betairidovirinae (Iridovirus, blue; Chloriridovirus, brown) subfamilies. Virus species and isolates are indicated by abbreviations, listed in Table 2. Members of accepted species are shown in bold typeface. The tree was constructed using maximum likelihood analysis using IQ-TREE open source software [9] under optimum substitution model LG+I+G4 according to Bayesian Information Criterion (BIC) [10].and the concatenated amino acid (aa) sequences of 26 core genes (19,773 aa characters including gaps) from 45 completely sequenced iridovirus genomes. The tree was midpoint rooted and branch lengths are based on the number of inferred substitutions, as indicated by the scale bar. The branch points that separate the iridovirid genera are supported by bootstrap values greater than 99%. For other branch points all bootstrap values are >70% except for those displaying high levels of amino acid similarity, e.g., TFV vs. BIV/GGRV, 66%; PPIV vs. CMTV/2013/NL et al., 49%; TRBIV vs. RSIV et al., 57%; and LYCIV vs. TRBIV et al., 56%. Scale bar represents amino acid substitutions per site. This figure was published as an ICTV report [1,2].