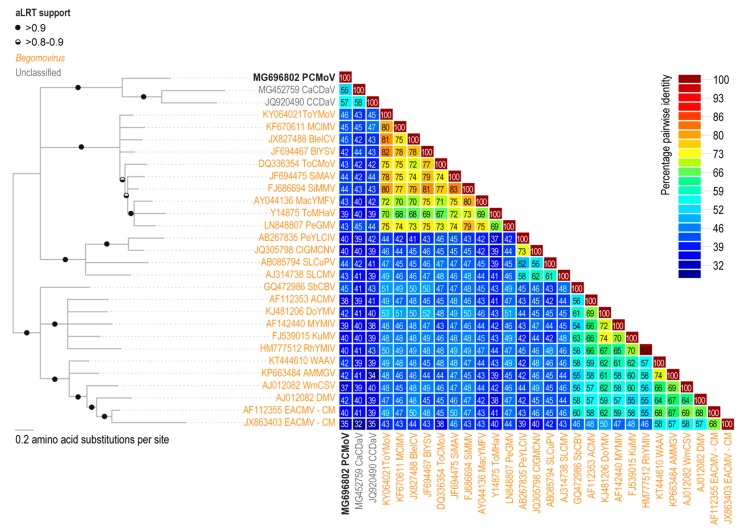
Figure 3.
Midpoint rooted Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree inferred using the substitution model rtREV+G for the MP amino acid sequences and aLRT test for branch support coupled with percentage pairwise identity matrix of the MP amino acid sequences. The sequences used for both analysis are those encoded by the following: African cassava mosaic virus (ACMV), asystasia mosaic Madagascar virus (AMMGV), blainvillea yellow spot virus (BlYSV), blechum interveinal chlorosis virus (BleICV), CaCDaV, CCDaV, clerodendrum golden mosaic China virus (ClGMCNV), deinbollia mosaic virus(DMV), dolichos yellow mosaic virus (DoYMV), East African cassava mosaic virus-Cameroon (EACMV-CM), Kudzu mosaic virus (KuMV), macroptilium yellow mosaic Florida virus (MacYMFV), melon chlorotic mosaic virus (MClMV), mungbean yellow mosaic India virus (MYMIV), PCMoV, pepper golden mosaic virus (PeGMV), pepper yellow leaf curl Indonesia virus (PeLCIV), rhynchosia yellow mosaic India virus (RhYMIV), sida micrantha mosaic virus (SiMMV), sida mosaic Alagoas virus (SiMAV), soybean chlorotic blotch virus (SbCBV), squash leaf curl Philippines virus (SLCuPV), Sri Lankan cassava mosaic virus (SLCMV), tomato chlorotic mottle virus (ToCMoV), tomato mosaic Havana virus (ToMHaV), ToYMoV, watermelon chlorotic stunt virus (WmCSV), and West African asystasia virus (WAAV).