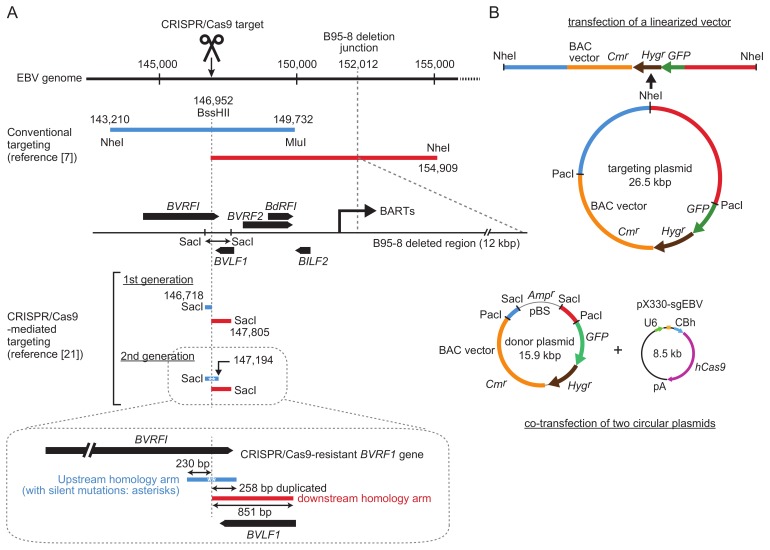
Figure 2.
Comparison of homology arm lengths used for conventional and CRISPR/Cas9-mediated EBV-BAC cloning. (A) Homology arms employed by conventional targeting [24] and CRISPR/Cas9-mediated targeting [21] are illustrated by preserving their relative sizes. Upstream homology arms are in blue, and downstream homology arms are in red. Nucleotide numbers correspond to those of the B95-8 strain of EBV (V01555.2). EBV ORFs around the transgene insertion site are indicated as black arrows. Restriction enzyme sites used for targeting vector construction are indicated. Upstream and downstream homology arms of the second generation donor plasmid, together with the locations of BVRF1/BVLF1 ORFs, are illustrated in detail at the bottom. (B) Schematic representation of a targeting plasmid (top, for conventional targeting) or a donor plasmid (bottom, for CRISPR/Cas9-mediated targeting). Note their different sizes.