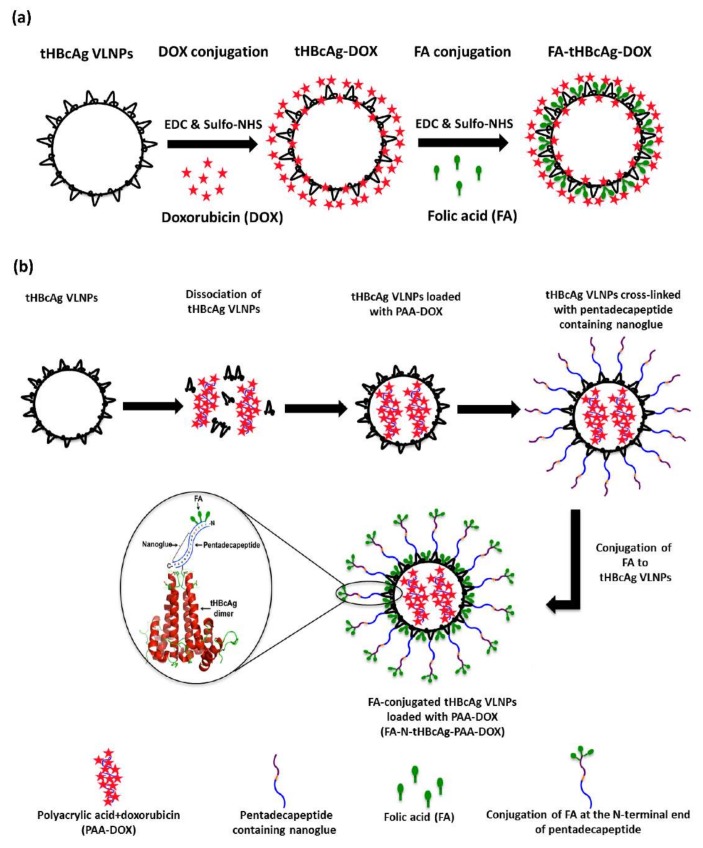
Scheme 1.
Schematic representation of two different drug delivery systems based on VLNPs. (a) Dual conjugated tHBcAg VLNPs. tHBcAg VLNPs possess several accessible Glu, Asp and Lys residues for the conjugation of drug and cancer targeting ligands. The carboxylate groups of Glu and Asp are used to conjugate doxorubicin (DOX). DOX-conjugated VLNPs are then conjugated with folic acid (FA) at Lys residues; (b) pH-responsive tHBcAg VLNPs. tHBcAg VLNPs are dissociated into tHBcAg dimers using urea. DOX is mixed with polyacrylic acid (PAA) and added into the mixture containing dissociated tHBcAg dimers. When the urea is removed by dialysis, tHBcAg dimers reassemble into nanoparticles and package PAA-DOX. tHBcAg VLNPs loaded with PAA-DOX are then cross-linked with a pentadecapeptide containing the nanoglue. Cross-linked VLNPs are then conjugated with FA via the three Lys residues located at the N-terminal end of the pentadecapeptide using EDC [1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethyl-aminopropyl)-carbodiimide hydrochloride] and Sulfo-NHS (N-hydroxysulfosuccinimide).