Fig. 4.
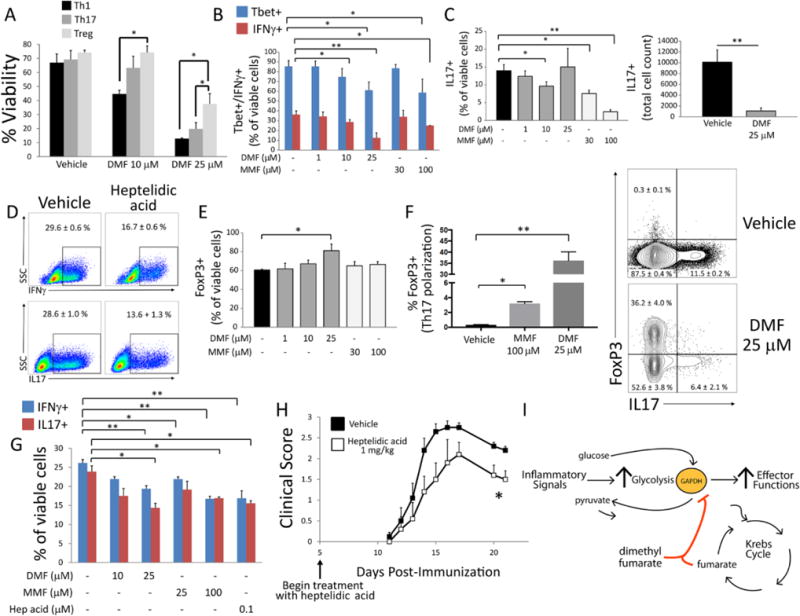
DMF and MMF differentially impact survival, differentiation, and effector function of metabolically distinct lymphocyte subsets. (A to F) Mouse naïve CD4+ lymphocytes were activated for four days with anti-CD3/CD28 antibodies under Th1-, Th17-, or Treg-cell-polarizing conditions. Cells were treated with indicated doses of DMF, MMF, or heptelidic acid on day 0 and assayed by flow cytometry on day 4. (A) DMF disproportionately decreased survival under Th1- and Th17-cell vs. Treg-cell polarizing conditions, as assessed by LIVE/DEAD aqua stain. Data represent mean ± SEM of three experiments performed in duplicate or triplicate. (B and C) DMF/MMF decreased the proportion of Tbet+ and IFNγ+ cells under Th1-cell-polarizing conditions (B) and of IL-17+ cells under Th17-cell-polarizing conditions (C, left). DMF (25 μM) produced variable results under Th17-cell-polarizing conditions, likely due to high toxicity at that dose, but nonetheless caused a significant decrease in total IL-17+ cell count (C, right). Data represent mean ± SEM of three experiments performed in duplicate or triplicate. (D) Representative flow cytometric plots demonstrating that low-dose (0.5 μM) heptelidic acid replicated the effect of DMF/MMF on IFNγ and IL-17 expression under Th1- and Th17-cell-polarizing conditions, respectively. Toxicity limited the testing of higher doses. Values represent mean ± SEM of a triplicate experiment. (E) In contrast to effects on Th1 and Th17 cells, DMF increased the proportion of FoxP3+ cells under Treg-cell-polarizing conditions. Data represent mean ± SEM of three experiments performed in duplicate or triplicate. (F) DMF/MMF produced a reciprocal increase in FoxP3+ cells under Th17-cell-polarizing conditions. Bar graph (left) and representative flow cytometric plot (right) from a triplicate experiment. Data represent mean ± SEM. (G) Mouse naïve CD4+ lymphocytes were activated under Th1- or Th17-cell-polarizing conditions for three days and then treated overnight with the indicated drug. Expression of IFNγ and IL-17 was then assessed by flow cytometry. Data represent mean ± SEM of a triplicate experiment. (H) Daily I.P. treatment with heptelidic acid attenuated the course of EAE. Data were pooled from five mice per group and represent mean ± SEM for each time point. (I) Proposed model of immune modulation by DMF, which may exploit a physiologic negative feedback function of endogenous fumarate. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison (A); one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison (B, C, E–G); and Mann–Whitney U test (H).
