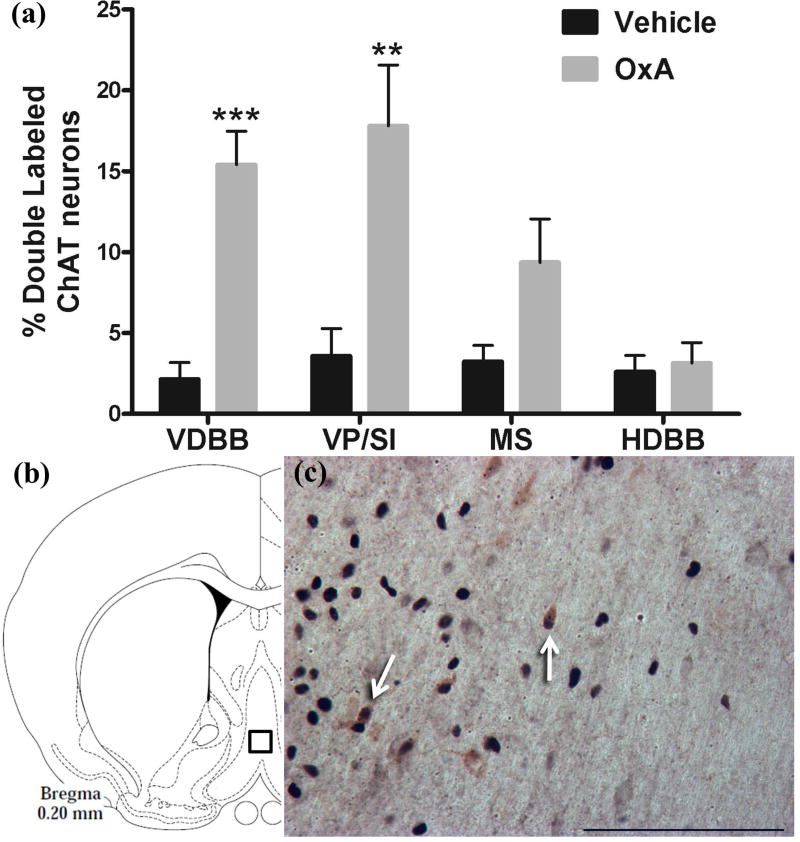
Fig. 4.
Activation of cholinergic neurons in the basal forebrain by intranasal OxA administration. (a) Percentage of double-labeled (c-Fos/ChAT) neurons relative to the total number of ChAT positive neurons within the VDBB, VP/SI, MS, and HDBB after treatment with intranasal saline (vehicle; all regions, n=8 rats) or intranasal OxA (50 µl, 100 µM; all regions, n=8 rats). Intranasal OxA significantly increased the percentage of dual-labeled ChAT neurons in the VDBB and VP/SI compared to vehicle treated controls. (b) Schematic indicating the approximate location (black-outlined square) within the VDBB where c-Fos/ChAT counts and photomicrographs were obtained. (c) Typical dual-label immunohistochemistry for c-Fos (blue/black) and ChAT (brown) neurons within the VDBB (arrows). Abbreviations: OxA, orexin-A; ChAT, choline acetyltransferase; VDBB, vertical limb of the diagonal band; VP/SI, ventral pallidum/substantia innominata; MS, medial septum; HDBB, horizontal limb of the diagonal band. Scale bar represents approximately 100 µm (c). Error bars represent SEM. ***p<0.001, **p<0.01