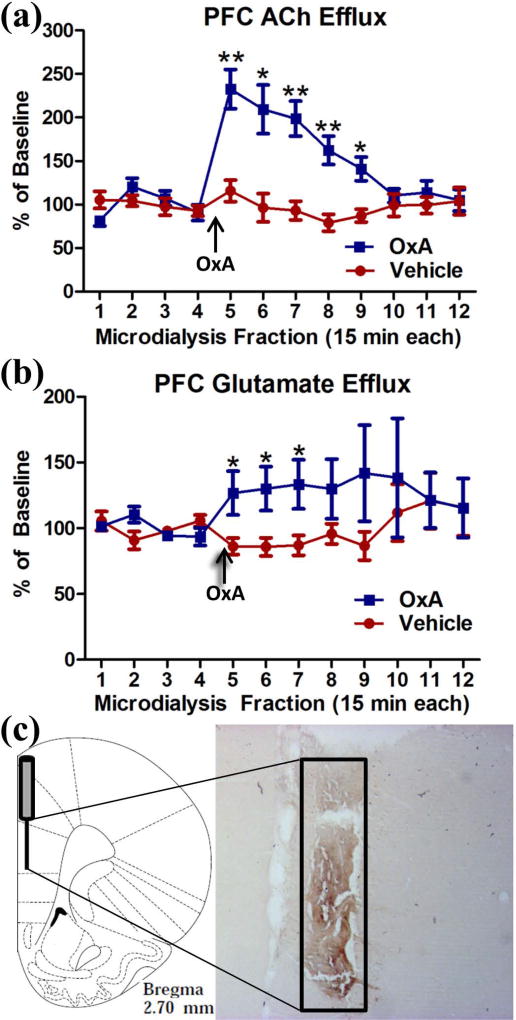
Fig. 5.
Effect of intranasal OxA administration on ACh and glutamate efflux in the PFC. (a) Intranasal OxA (50 µl, 100 µM; n=10 rats) treatment after baseline collections (arrow) significantly increased ACh efflux compared to intranasal vehicle (saline; n=10 rats). A significant increase in ACh efflux was observed from time points five through nine versus vehicle (b) Intranasal OxA (arrow; n=10 rats) also significantly increased glutamate efflux within the prefrontal cortex compared to treatment with intranasal saline. The significant effect lasted from time points five through eight versus vehicle treatment. (c) Diagram indicating the approximate probe placement within the PFC for each of the animals that underwent microdialysis. Typical probe placement in the PFC is indicated on AChE background-stained section from an animal that underwent two microdialysis sessions. Abbreviations: PFC, prefrontal cortex; ACh, acetylcholine; in, intranasal; OxA, orexin-A. Error bars represent SEM. **p<.01, *p<.05