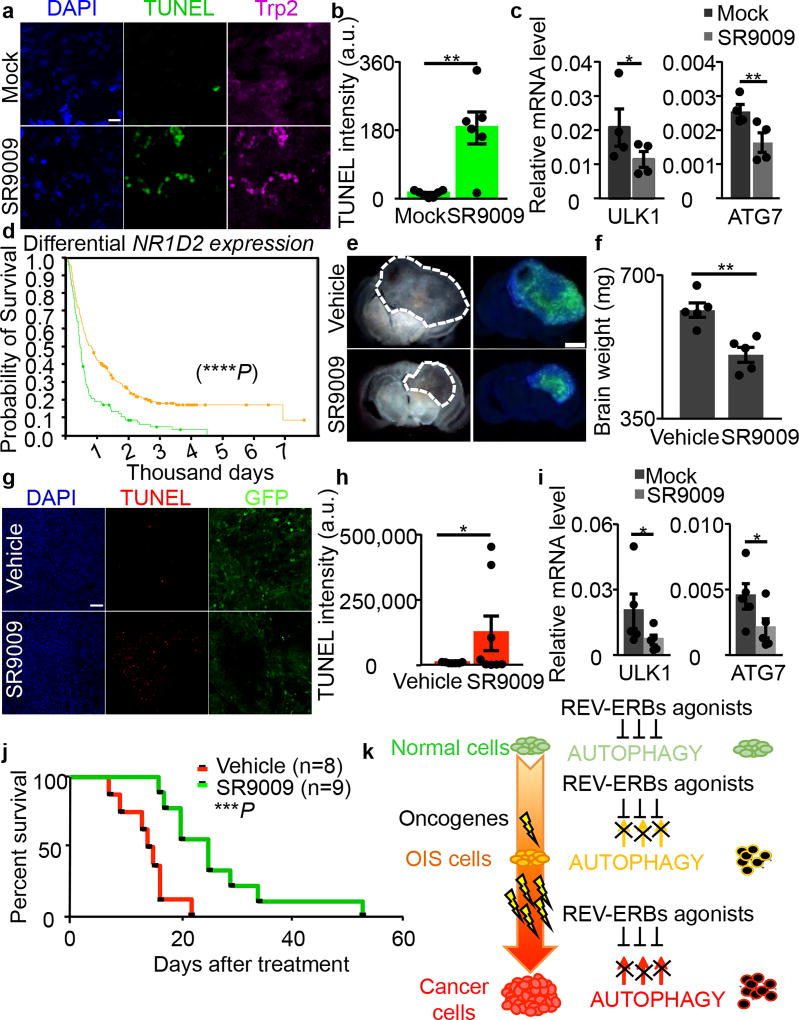
Figure 4. SR9009 impairs viability of NRAS-driven naevi, glioblastoma growth and extends survival.
a–b, SR9009 treatment induces apoptosis in vivo in NRAS naevi as assayed by immunofluorescence analysis (representative images of two independent experiments with similar results, Trp2 melanocytic marker and TUNEL, Mann–Whitney test one-tailed **P=0.0058, n=biologically independent samples, n=7 mock, n=6 SR9009, 12 days SR9009 20 µM, four mice). Scale bar 10 µm. c, Autophagy genes are downregulated upon treatment of NRAS naevi n=4 mice; Mann–Whitney one-tailed ULK1 *P=0.0249, ATG7 **P=0.007. d, REV-ERBβ expression correlates with survival in brain cancer patients (n= biologically independent samples, yellow line intermediate expression n=224, green line downregulated n=119 NIH Rembrandt database; Log-rank two-sided ****P<0.0001;). e–f, SR9009 treatment impairs in vivo growth of glioblastoma (representative images of one experiment n=5 mice, 6 days, 200mg/kg b.i.d.; Mann-Whitney test one-tailed **P=0.004). g–h, SR9009 induces apoptosis in glioblastoma as shown by TUNEL assay; tumor cells are GFP-positive (representative images of one independent experiment, 6 days 200mg/kg b.i.d., Mann–Whitney test one-tailed *P=0.02; n=biologically independent samples, n=7 mock, n=8 SR9009, five mice). i, In vivo treatment with SR9009 results in downregulation of main autophagy genes (6 days, 200mg/kg b.i.d., n=5 mice, Mann-Whitney test one-tailed *P=0.0476). j, SR9009 improves survival of mice affected by glioblastoma. SR9009 100mg/kg, Vehicle n=8 SR9009 n=9 mice; log-rank two-tailed ***P=0.0009. k, Scheme illustrating how REV-ERB agonists selectively affect OIS and cancer cells. All panels mean ± s.e.m.