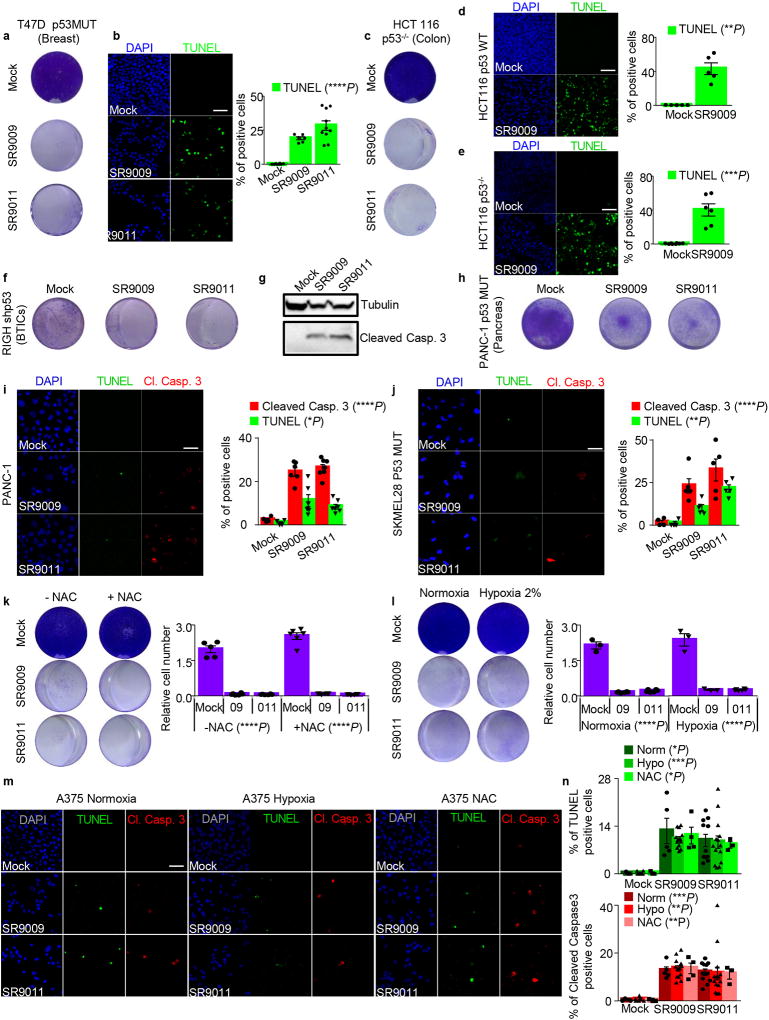
Extended Data Figure 2. Induction of apoptosis by REV-ERBs agonists is p53 and oxidative stress independent.
a–j, REV-ERBs agonists treatment triggers apoptosis independently of p53 status as showed by proliferation assay (7 days 20 µM; a,c,f,h) and TUNEL assays (b,i,j 3 days, 20 µM) in cancer cell lines affected by different types of p53 alterations. N= biological independent samples T47D n=8 (mock), n=6 (SR9009), n=10 (SR9011) One-way ANOVA test ****P<0.0001, PANC-1 n=4 (mock), n=6 (SR9009), n=7 (SR9011) one-way ANOVA test TUNEL *P=0.0108, Cl. Caspase 3 ****P<0.0001; SKMEL28 n=4 (mock), n=5 (SR9009, SR9011) one-way ANOVA test TUNEL ****P<0.0001, Cl. Caspase 3 **P=0.0035,).; d–e, Apoptosis is induced in both WT and p53 null HCT116 cell (TUNEL assay 4 days, 20 µM mean ± s.e.m., n= biological independent samples Mann–Whitney test one-tailed HCT116 WT n=5 (mock, SR9009) **P=0.004; HCT116 p53 KO n=8 (mock), n=6 (SR9009) ***P=0.0003); f, Immunoblot analysis of cleaved Caspase 3 shows that REV-ERBs agonist triggers apoptosis in RIGH cell line (one experiment). k, Co-treatment with the reducing agent N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC 10mM) does not rescue A375 viability (20 µM 7 days, n= biological replicates n=5 (mock -NAC), n=6 (all others dot plots) one-way ANOVA test ****P<0.0001). l Similar results are obtained also under hypoxic condition (20 µM, 6 days, n= biological replicates n=3 (mock -NAC, mock hypoxia, 09 hypoxia), n=6 (09 normoxia, 011 normoxia and hypoxia) one-way ANOVA test ****P<0.0001). m–n, Hypoxia or co-treatment with NAC does not alter REV-ERBs agonists ability to induce apoptosis in A375 (one-way ANOVA test, n= biological independent samples, n=3 mock, n=5 SR9009, n=11 SR9011 TUNEL normoxia, *P=0.0432, Cl. Caspase 3 ***P=0.0004; n=6 mock, n=13 SR9009, n=14 SR9011 hypoxia TUNEL ***P=0.0005, Cl. Caspase 3 *P=0.0028; n=3 mock, n=4 SR9009, n=3 SR9011 NAC TUNEL *P=0.0104, NAC Cl. Caspase 3 **P=0.0042; All scale bars 50 µm. All panels three biological independent experiments with similar results, except otherwise specified. All the data are plotted as mean ± s.e.m. Norm= Normoxia; Hypo= Hypoxia. For gel source data, see Supplementary Fig. 1.